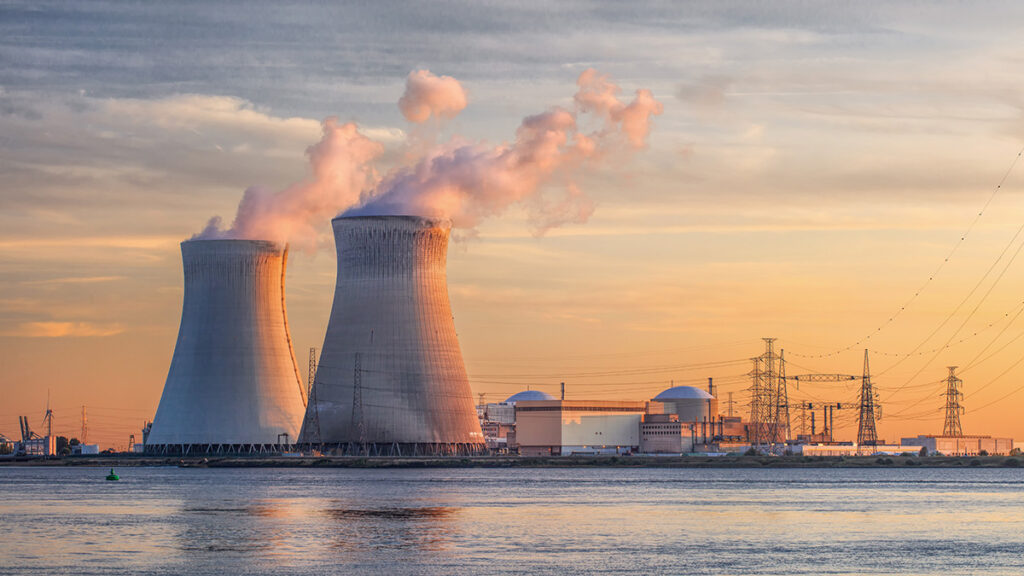
Nuclear power has proven itself to be an efficient large-scale source of energy for decades. While both fission and fusion reactions can produce energy, the practicality of building the reactors depends on the process and reaction containment procedure. Fission power can be controlled, and despite its disadvantages, such as radiation, it is widely used in nuclear power reactors. Fusion power, on the other hand, offers great potential; however, controlling a fusion reaction is difficult. Consequently, harnessing fusion power is still in its experimental phase.
The difficulty of harnessing nuclear fission and fusion power results from the engineering challenge of building nuclear reactors that adhere to regulatory standards and structural requirements. Below, we will discuss how orbital welding ensures the highest quality welds in nuclear reactors and other components.
Exploring Nuclear Fission and Fusion Power
Nuclear Fission
Fission reactors are the most common nuclear reactors, and they produce a tremendous amount of energy using fuel such as uranium or plutonium. During the reaction, energy is released when the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. When struck by a fission neutron, subsequent atoms also undergo a fission reaction creating a nuclear chain reaction. In a nuclear reactor, this reaction can be controlled to release energy at a supervised rate. The energy thus released heats water into steam that rotates a turbine for power generation.
The nuclear fission process is relatively clean and requires a small amount of fuel to produce a large amount of energy. However, containing radioactivity and disposing of radioactive waste presents a challenge. Similarly, the extreme temperature and pressure conditions necessitate that structural components stay in peak condition. When welding components like pressure vessels, piping systems, steam generators, fittings, and fuel storage or waste disposal containers, welders must follow a strict procedure.
Nuclear Fusion
Fusion power essentially combines two atomic nuclei to release heat. The fusion reaction offers an alternative to counter the drawbacks associated with fission reactions since it can produce an unlimited amount of energy without the risk of any radiation or the trouble of radioactive waste disposal. Fusion reactors aim to contain the fusion reaction during the energy-harnessing process. But unfortunately, no one has been able to sustain a controlled and stable fusion reaction. Building a nuclear reactor and employing welding and other fabrication processes presents tremendous engineering challenges.
While nuclear welding standards have been set by organizations like ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) with BPVC (Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code) to ensure safety and quality, meeting these strict requirements can be difficult for welders. Employing an automated orbital welding process can provide an effective solution.
Nuclear Fusion vs Fission: The Comparison
The table below highlights the primary differences between nuclear fission and fusion processes.
| Nuclear Fusion vs Fission | ||
| Nuclear Fission | Nuclear Fusion | |
| Process | The nucleus of the atom splits into two or more smaller fragments | Atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus |
| Energy generation | Energy generates due to the atomic split | Energy is produced when atomic fusion occurs |
| Fuel | Heavy radioactive elements, such as Uranium-235 or plutonium-239 | Light isotopes of hydrogen such as deuterium and tritium |
| Reaction stability | Stable reaction with relatively low risk | Highly unstable reaction |
| Reaction control | The chain reaction can be controlled with the use of control rods | Difficult to control the extremely high temperature and pressure |
| Waste | Generates radioactive waste with long-term concerns | Generates short-lived radioactive waste |
| Commercial viability | Well-established and commercially viable technology for large-scale energy generation | Under research and development phase and not yet commercially viable for large-scale energy generation |
| Advantages | Affordable low-emission energy generation | Clean and sustainable energy generation |
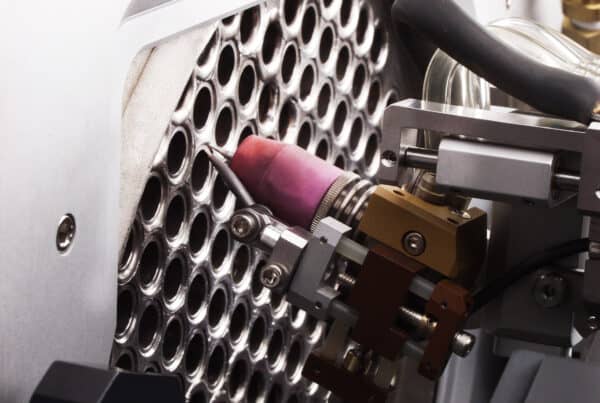
The Role of Orbital Welding in the Nuclear Industry
When performing nuclear welding, considerations include:
- Welding process used with thick/thin-wall welding capability
- The material that makes the nuclear plant components
- Corrosion possibility in the component due to mechanical stress or the material content
- Weld strength desired
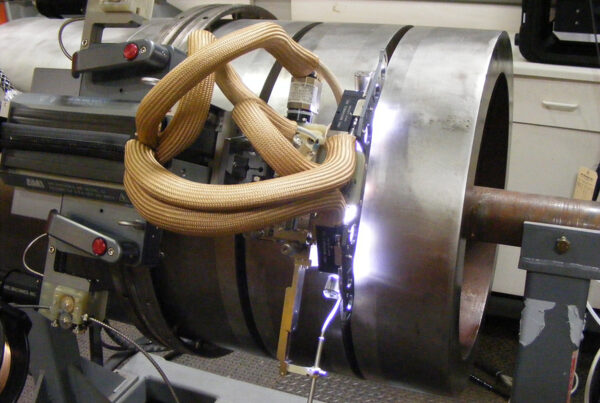
Because TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is suitable when welding pressure vessels, pipes, and tubes used in nuclear plants, it has been the traditional process. However, due to the manual limitations of TIG, orbital welding is preferred for performing high-spec welding for such critical components.
When considering nuclear fusion vs fission power plants, orbital welding provides common advantages:
- Weld accommodation for a wide range of materials, including titanium, Inconel, and stainless steel, that are commonly used in nuclear plants.
- Remote weld monitoring to control and optimize the weld parameters while keeping the operators safe from harmful radiation.
- Reduced risk of contamination with provision for a controlled welding environment.
- Specialized nuclear welding with custom weld heads such as Model 34 that provide the automation, control, and data acquisition capabilities for various welding processes and designs.
- Speed and repeatability to ensure high-quality results.
Achieve High-Quality Nuclear Welding Results
For narrow-gap welding, tube-to-tube sheet welding, or other nuclear welding needs, orbital welding produces unparalleled output. The control and precision offered with automated processes such as orbital welding can reduce weld defects while enhancing weld strength. When thinking of nuclear fusion vs fission power, either reactor must ensure safe and effective operation. Safety, monitoring, and reliability offered by orbital welding allow manufacturers to meet strict nuclear welding standards for nuclear reactors and their ancillary equipment.
Arc Machines, Inc. is an industry leader in providing high-tech nuclear welding solutions. This includes advanced orbital weld heads and welding machines that foster optimal weld results. For inquiries regarding products, contact sales@arcmachines.com. For service inquiries, contact service@arcmachines.com. Arc Machines welcomes the opportunity to discuss your specific needs. Contact us to arrange a meeting.