Since the inception of orbital welding in the 1960s, wide-ranging industries continue to adopt its advanced abilities. Industries that once relied on manual welding now leverage the benefits of greater precision and higher productivity through the automated approach of the orbital welding system. In critical applications like nuclear plants, petroleum pipelines, or food-grade applications, orbital welding systems can offer clean and error-free welds crucial to maintaining system integrity.
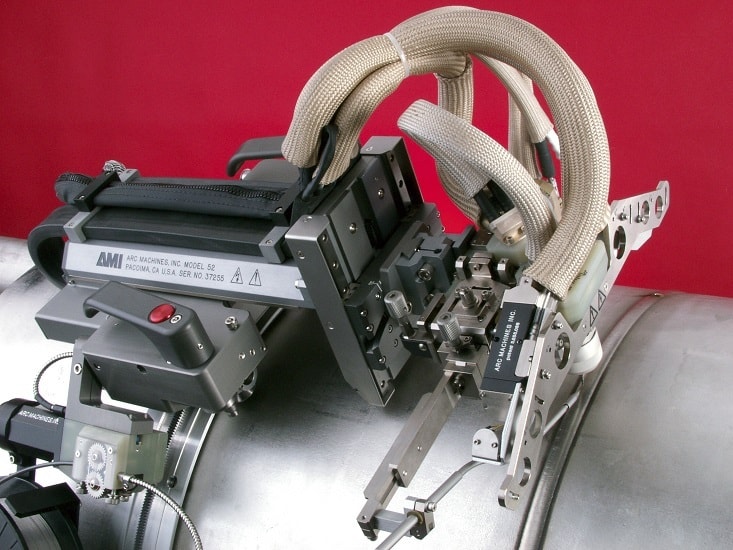
The orbital welding system is composed of various elements that enable parameter optimization during the weld. Here, we’ll explore the functions of these elements and their importance in creating a high-quality weld.