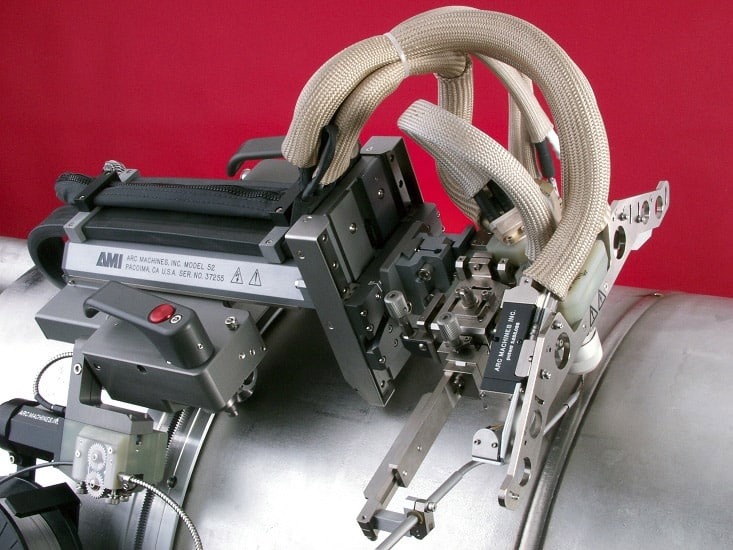
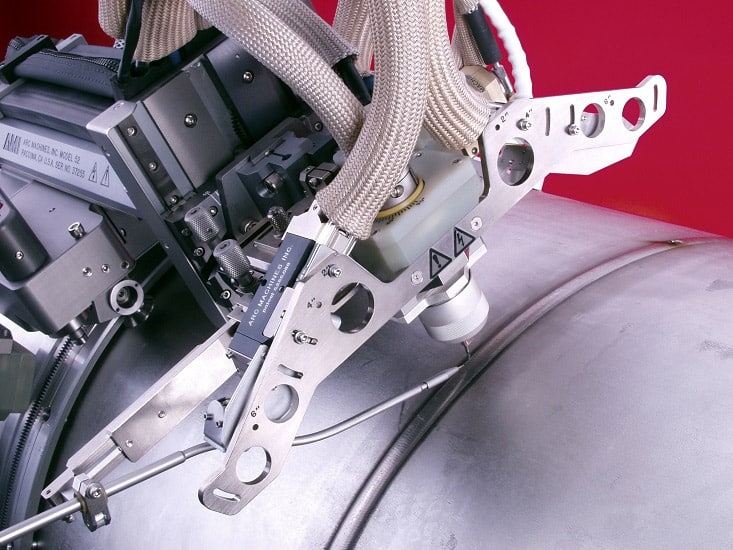
Welding thick metal workpieces is a challenging process, mechanically and economically. A conventional welding procedure is generally not effective for the metal thickness equal to or more than 12.5 mm (1/2 inch). Narrow gap welding (also known as narrow groove welding) can weld thicker base metals in a cost and time-efficient manner.
During welding preparation, the workpieces are beveled at an angle, commonly 30 to 37.5 degrees, for V-groove welding. The gap created is then closed by introducing filler metals during the welding process. This is the standard method used to join thick plates and pipe walls.
A narrow gap weld, on the other hand, uses a J-groove at each face of the metal to be welded. If the V-groove were applied on thick workpieces, the bevel angle would create a large gap. Instead, a narrow gap weld forms a U-shaped profile, which creates a small gap and can be welded with less filler material in a shorter time.
This efficiency makes narrow gap welding a popular choice among many industries for applications that include the fabrication of thick wall pipes, pressure vessels, and rotor shafts for steam turbines.