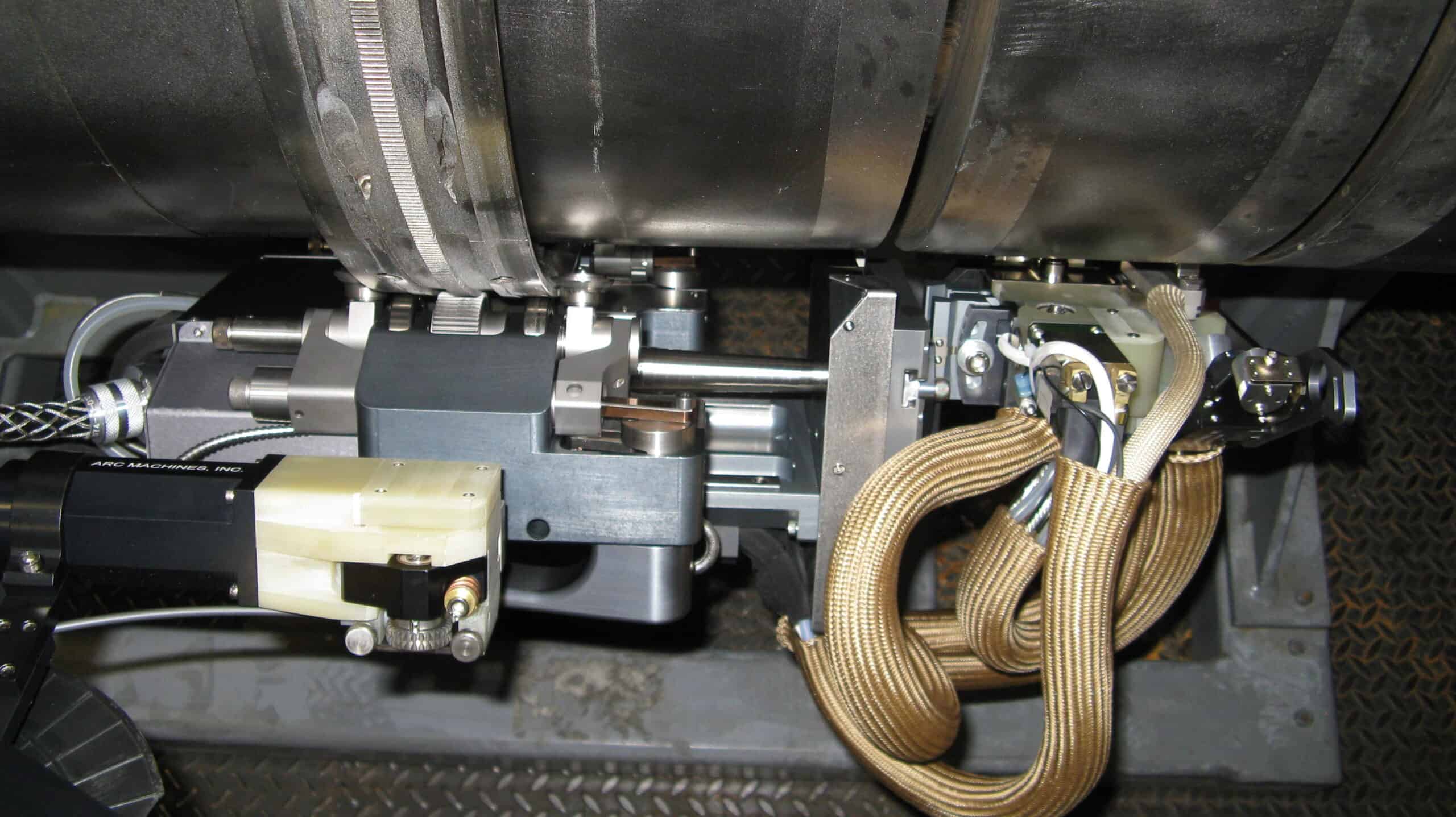
Welding is at the intersection of art, science, and labor. The artistry is in how the welder moves the molten puddle and controls weld formation. The labor is in cleaning the worksite and workpiece and preparing the joint for welding. The science is in the welding parameters that set the numbers the welder will be operating with. Automated orbital welding is different from other forms of welding because it places more emphasis on the science aspect of welding. It is simply a more precise form of welding where much of the process is handled by a machine. This means that it is critical that orbital TIG welding parameters are correct and set up correctly to ensure that welding is successfully completed to specification.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Setup
One of the things that is often overlooked in all forms of welding is the importance of the correct materials, proper setup, and cleanliness. The pressure to look to the bottom line in order to save on costs can interfere with welding before the welder ever gets started.
There are a few ways that cutting corners prior to welding can actually cost more money over the long-term:
- Cheaper metals often cost less, but are less consistent. In other words, these metals have a less consistent distribution of component elements. It is not unheard of for a company to buy low-grade steel and then spend more money welding and reworking welds due to quality issues than it would have cost to buy better metal to start with.
- For many, time is synonymous with money, which creates a temptation to cut corners in prep work. Rushing the machining of pipe before starting big bore pipe welding, for instance, can lead to a lot of expensive reworking of very long welds.
- Not taking the time to clean work materials and welding machines can lead to contaminated welds. Grease that is left on the workpiece or lack of routine maintenance on weld heads can cause the introduction of contaminants into welds that can cause weld defects. These welds almost always have to be repaired and sometimes completely removed and rewelded.
A common misconception is that orbital welding, by dint of being automated, makes it possible to skip some of the standard prep work prior to welding. In truth, the opposite is true. Orbital welding actually requires that prep work be done consistently and to a very high standard in order for the weld to form properly.
Orbital TIG welding is a consistent and reliable welding method for pipes and tubing, but it is not magic that allows welders to skip the basics of welding preparation. Understanding this fact is crucial to developing orbital TIG welding parameters.
Understanding Orbital TIG Welding Parameters
Developing orbital TIG welding parameters is in most respects nearly the same as developing parameters for most other types of welding. It begins with a project drawing that describes the stresses that will be in play across a welded joint, such as mechanical stresses, pressure, and the action of chemicals that will be involved once the project goes into operation.
These will determine the specification requirements for:
- Materials: The materials that will be used in the weld will be chosen on the basis of the physical stresses that they need to hold up under, as well as other stresses like corrosion. This will determine whether the materials needed are carbon steel, stainless steel, or something more exotic like Monel®, Inconel®, or a combination of these.
- Wire feed fill: The dimensions of the materials will determine if autogenous welding without the use of additional fill material is appropriate, or if the use of additional fill material fed into the weld as a wire is needed. If wire feed welding is determined to be appropriate, then the wire feed material will have to be carefully chosen to be compatible with the overall structural materials.
- Workpiece machining: If the work materials and their dimensions call for additional wire-fed fill material, then it is likely that the workpieces will need to be suitably machined for narrow groove welding.
- Weld preparation: In applications like high-purity pipe welding, every aspect of the weld before, during, and after welding must be kept free of contaminants. This means that the interior volume of a pipe or tube will need to be filled with purge gas during welding to prevent oxidation or contamination of the weld interior.
Once the materials, dimensions of the materials, and the use of the wire feed are decided, the more specific aspects of actually performing the weld can be determined. A weld schedule will lay out in detail such factors as:
- Amperage: The rate of the flow of electrons into the weld.
- Voltage: The measure of the amount of electrical pressure needed to overcome the resistance to begin current flow. This is effectively synonymous with arc length.
- Wire Speed: The speed at which wire flows into the arc and molten puddle.
- Travel Speed: The speed at which the weld head moves as it completes the weld.
- Oscillation: The rate of side-to-side movement of the tungsten electrode as the weld head moves.
- Gas Type: The most common shielding gas used in TIG welding is argon. However, helium can be used in applications where more heat is required. The choice between argon, helium, or a mix depends on the material and the thickness of what is to be welded.
- Gas Flow: The flow of gas is determined by the volumes that need to be shielded during welding, the travel speed, and the type of gas used.
Together, these and other factors comprise a welding schedule that is a rough guide to how an individual weld should be completed. Orbital TIG welding manufacturers generally have libraries of weld schedules developed for their weld heads and power supplies for use with various joint types and materials. If they do not have one for a particular application, then an orbital welding machine manufacturer is usually happy to work with a buyer to develop a basic weld schedule for a unique application.
Orbital TIG welding parameters are detailed welding guides that are tailored to each individual weld required on a project. They can be thought of as weld schedules that have been signed off on by the project welding engineer and project manager. It is this final sign-off that creates an orbital TIG welding parameter. Developing new orbital TIG welding parameters requires in-depth and detailed work. A company that is new to orbital welding will want to rely on the experience of their orbital welding equipment provider.
Arc Machines, Inc. has decades of experience creating orbital TIG welding schedules for our clients. To develop a custom orbital welding schedule or for help finalizing orbital TIG welding parameters, contact us to arrange a meeting.