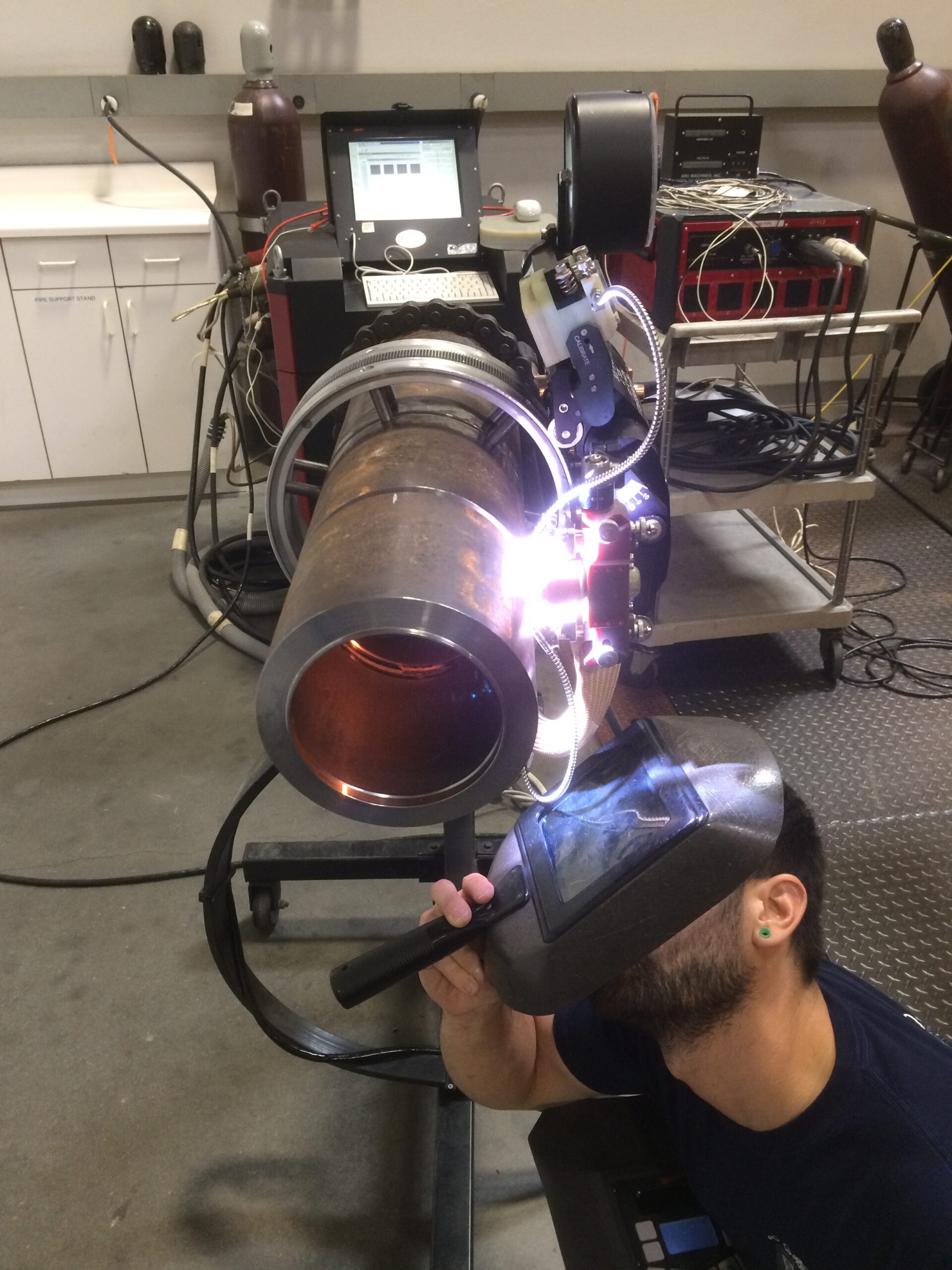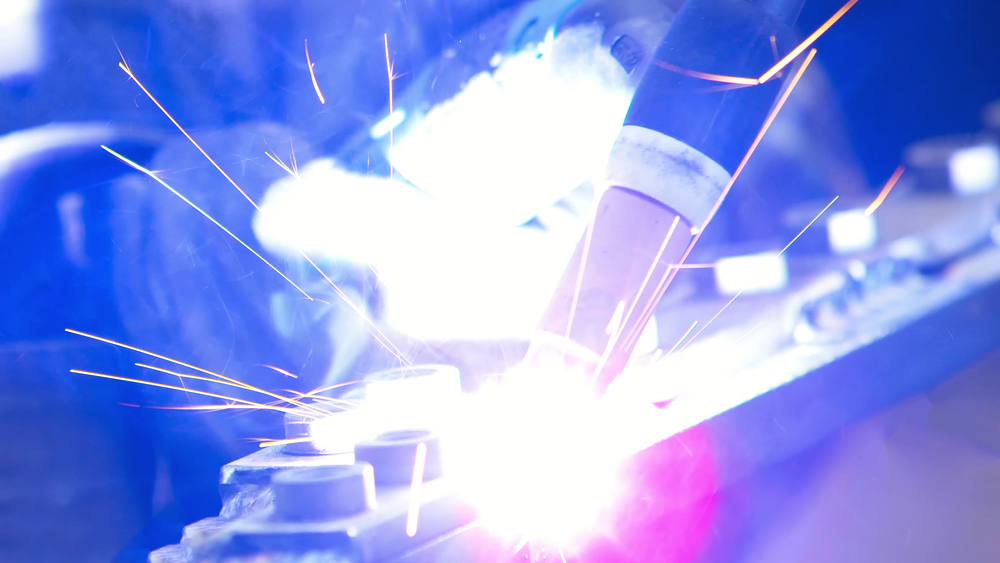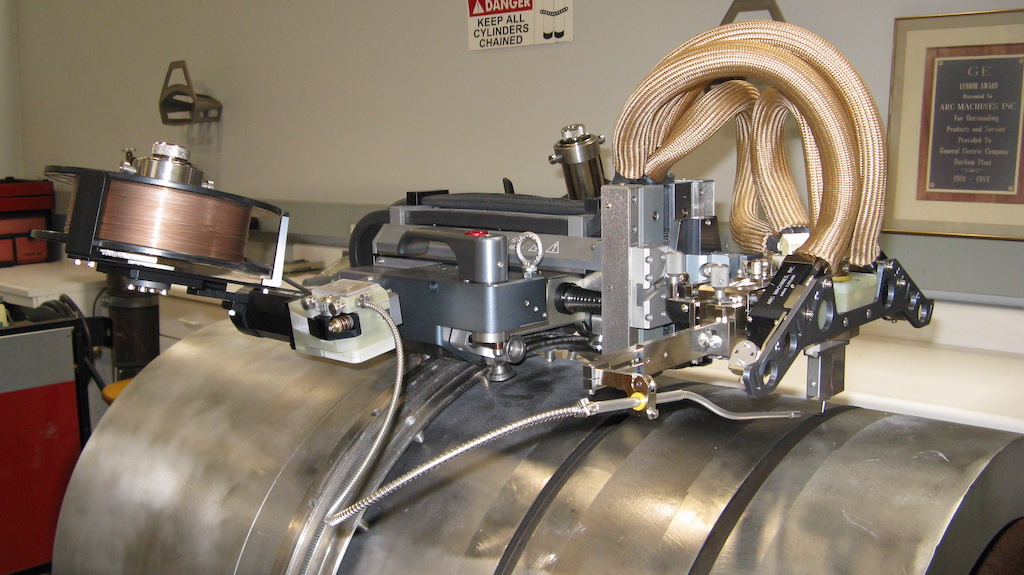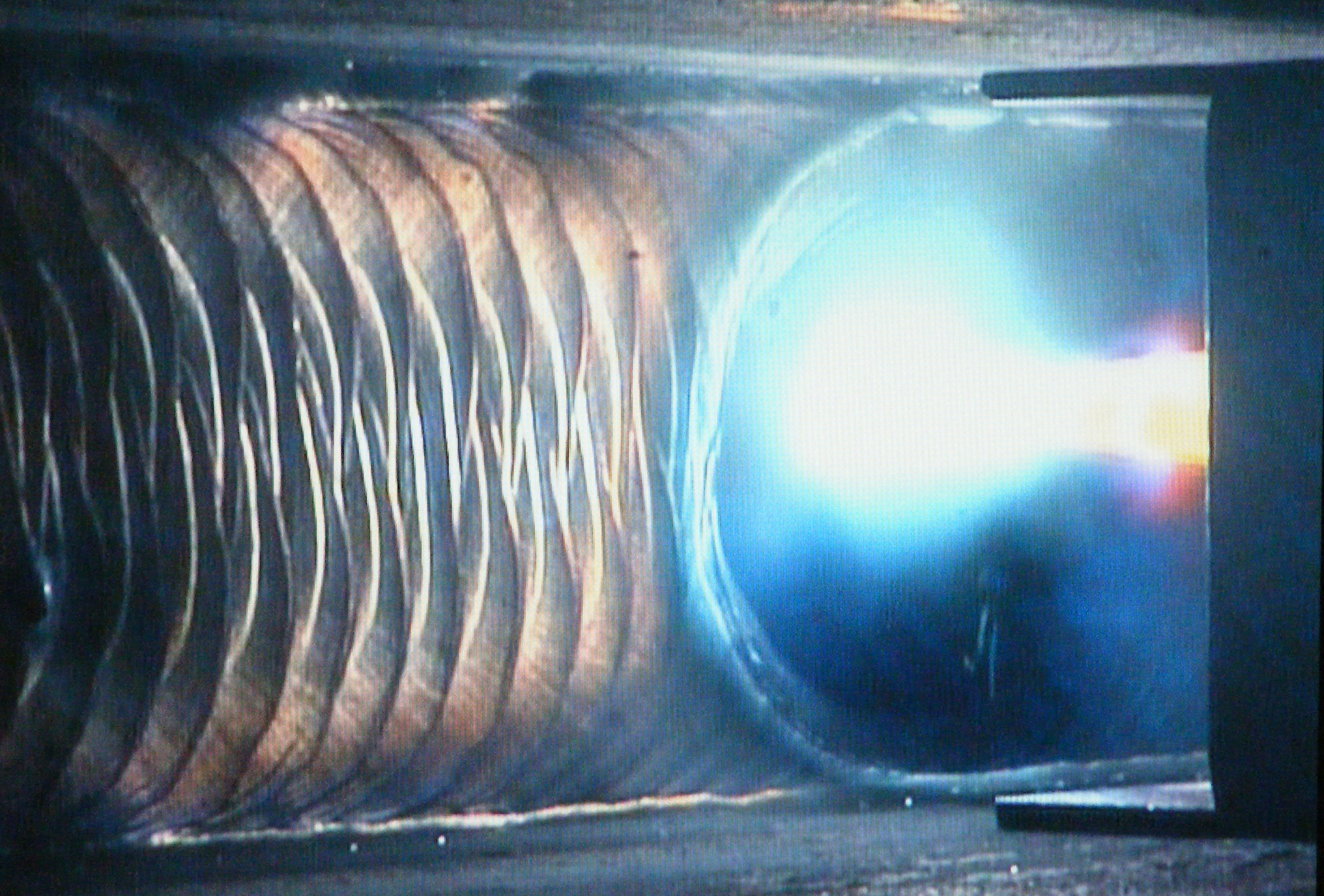
The term “weld pool” designates the molten puddle of metal liquified by the welding arc. It can be formed from the surface metal of the workpiece, filler metal introduced to the arc, or a combination of the two. In each case, the weld pool is subject to dynamics that are…