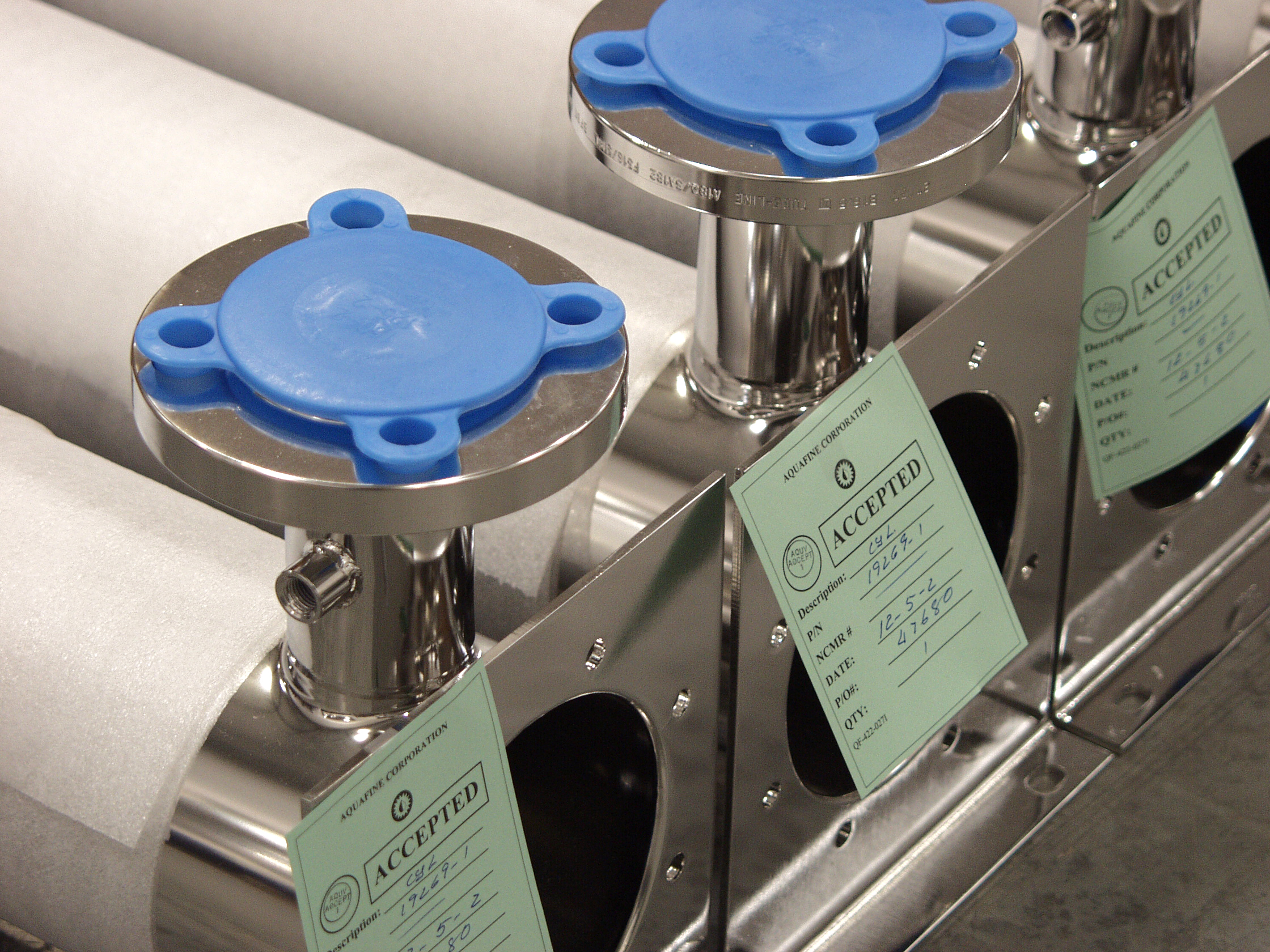


Blogs about Orbital Welding techniques and best practices.
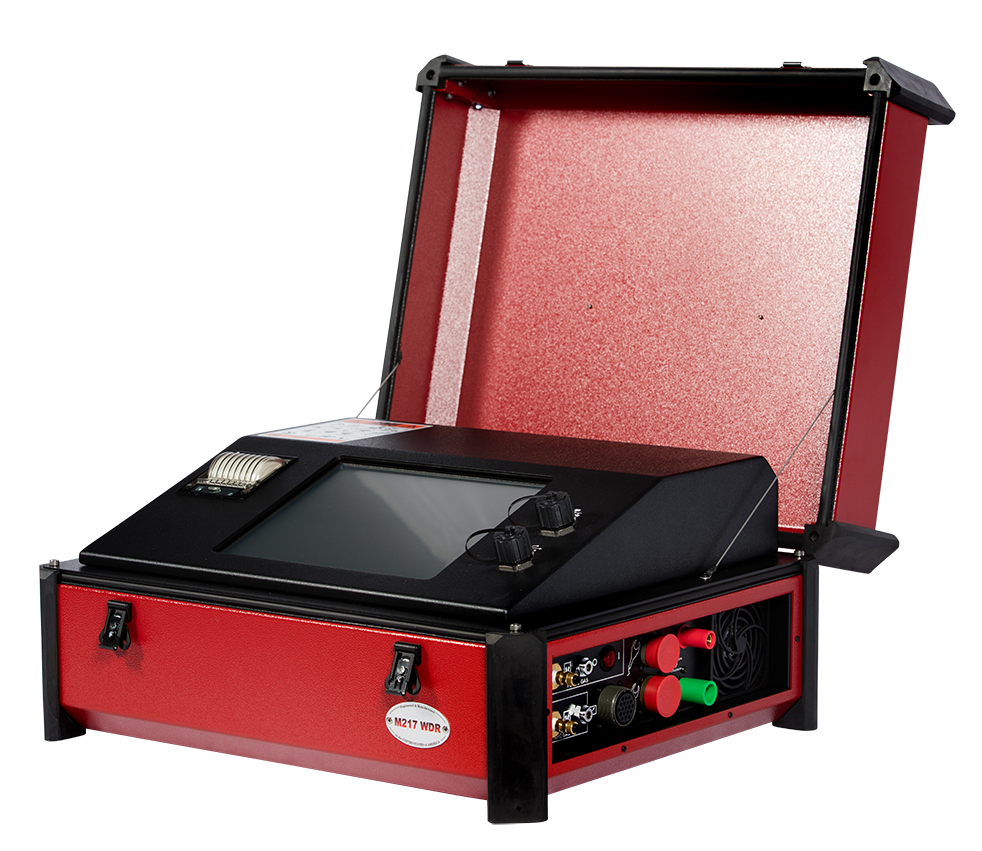


In welding, the power supply serves the function of regulating current and voltage for different arc welding applications. It is connected to the weld head, where the electric output transfers to the workpiece to melt and fuse pieces together. The consistent electric output is responsible for delivering a weld result…
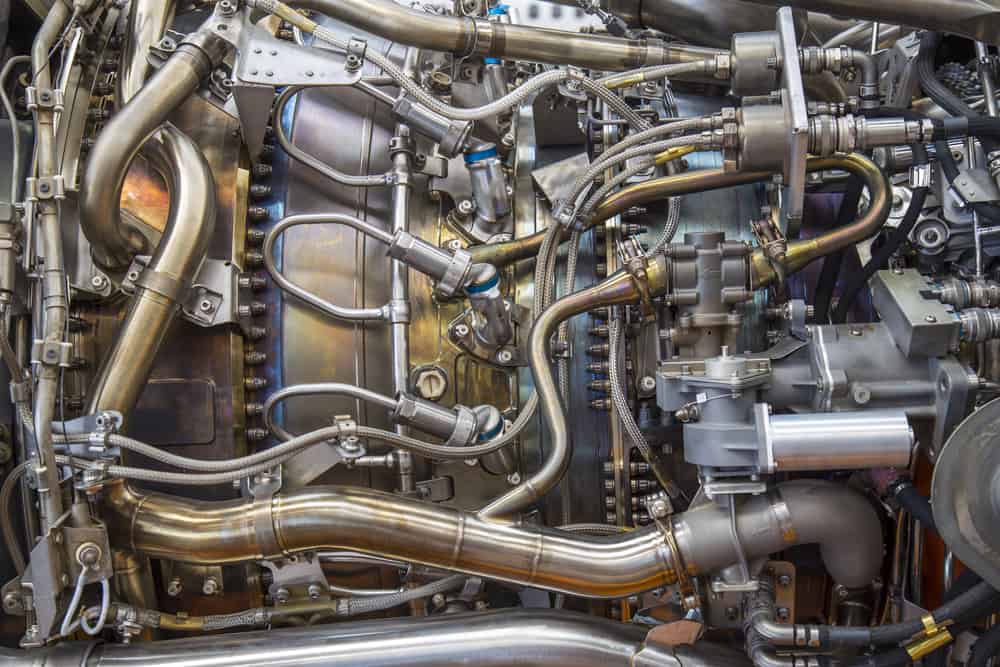

Fusion welding is any welding technique that heats two pieces of material to their melting point and joins them together while molten. This term can be a subject of confusion as engineers may use it as a blanket term to refer to all types of arc welding (which is technically…
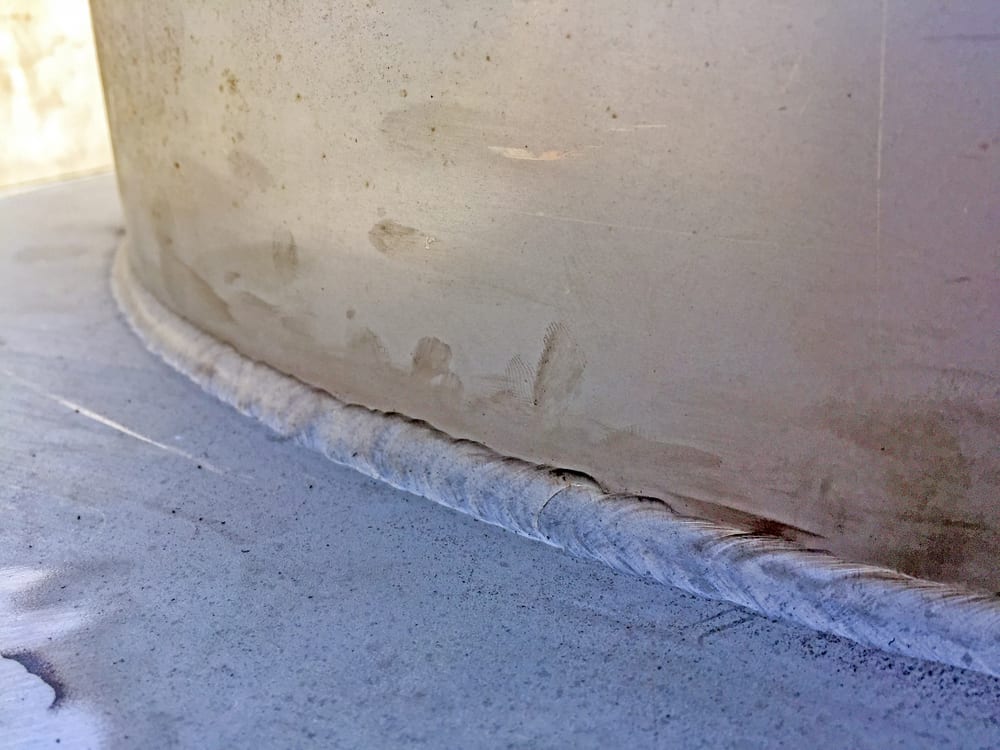

Heat is a complicated subject in welding. If the heat is too low, you will face problems achieving the required penetration. On the other hand, with high heat, you will have issues like cracking, spattering, and undercutting. Undercut in welding (or welding undercut) is a commonly observed defect—especially when welding…

Steel tubing is used everywhere—from refineries to aerospace to pharmaceuticals. It safely and reliably transports process fluids from one point to another. When welding steel tubing, welders have to make sure that the mechanical properties of the metal are not compromised so it can fulfill the reason for use in…
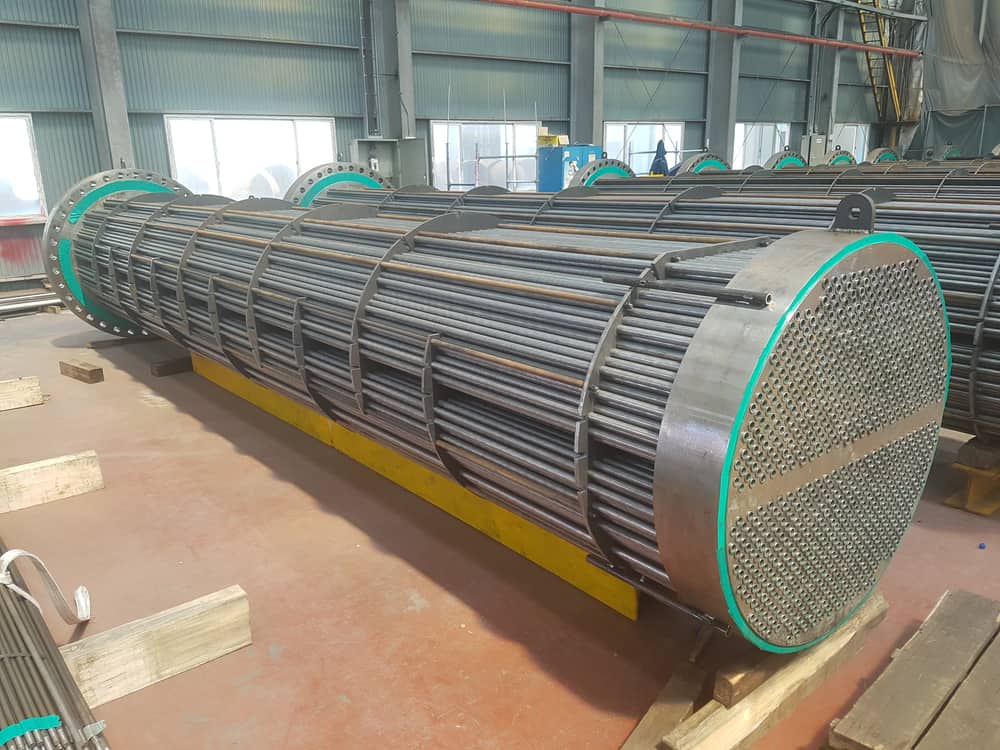

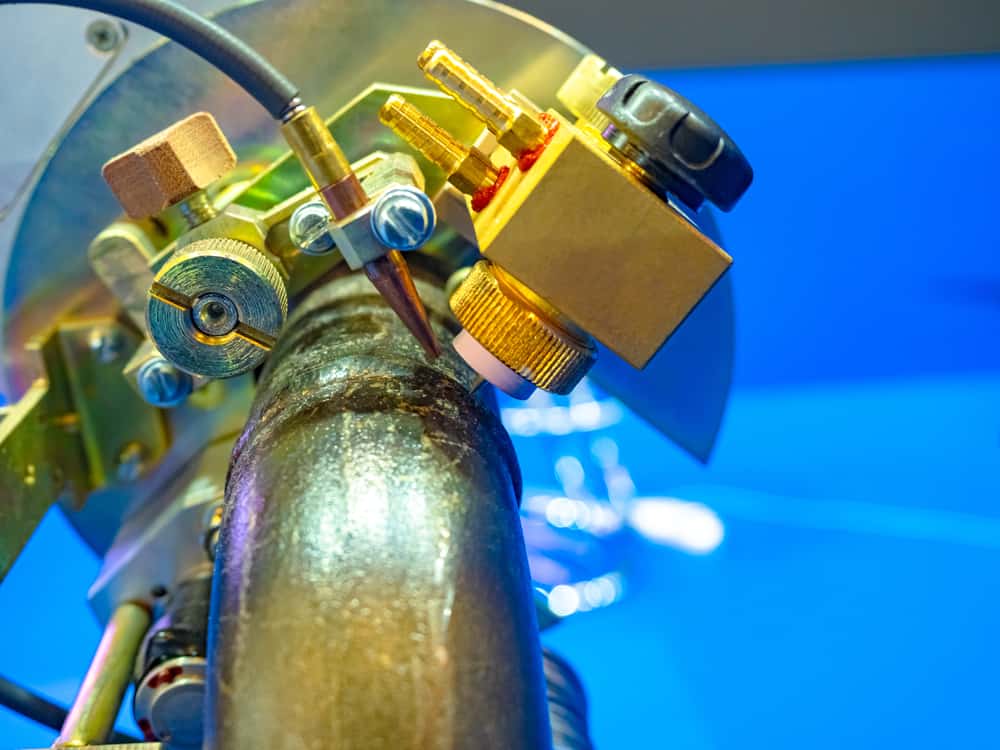

Heat exchangers are exactly what they are called: devices that transfer heat from one medium to another and heat exchangers find wide use in power generation and other industries. Tubesheets are simply sheets of metal perforated with holes that metal tubes can pass through at either end of a heat…

The history of pipe and tube production dates back to the 1900s when a process like hot-rolling was used for large-scale manufacturing. Since then, technologies like welding and seamless manufacturing have allowed the production of a much larger scale of pipes and tubes. Welding accounts for over half of all…