Welding originally referred to forge welding. Heating metal in a furnace and hammering on it until the pieces merged. Now, the term most often refers to arc welding and additional clarification is needed if you’re talking about traditional forge welding or welding using a gas such as oxyacetylene. Advancements in welding technology have made arc welding the new standard that everyone refers to.
Technology though marches ever onwards, and new advancements in welding technology make arc welding ever more versatile and sophisticated. Digital collection of welding data allows welding parameters to be dialed in ever more closely, higher quality power supplies allow for smoother welds, and automation is removing human error, and the need to rework workpieces to correct errors. Advancements in welding technology are making arc welding safer, more reliable, and the resulting welds of higher quality.
Automation and Digitalization in Welding
Arc welding remains the most widespread and preferred welding process in industry. While there are newer welding processes like laser and electron beam welding their adoption has been limited due to the expense and relative inflexibility of these systems. While they are technically newer than arc welding, both welding processes date back to the 1960s, and can hardly be considered new advancements in technology. Instead the latest advancements in welding technology have been in the form of automation and increasing use of data.
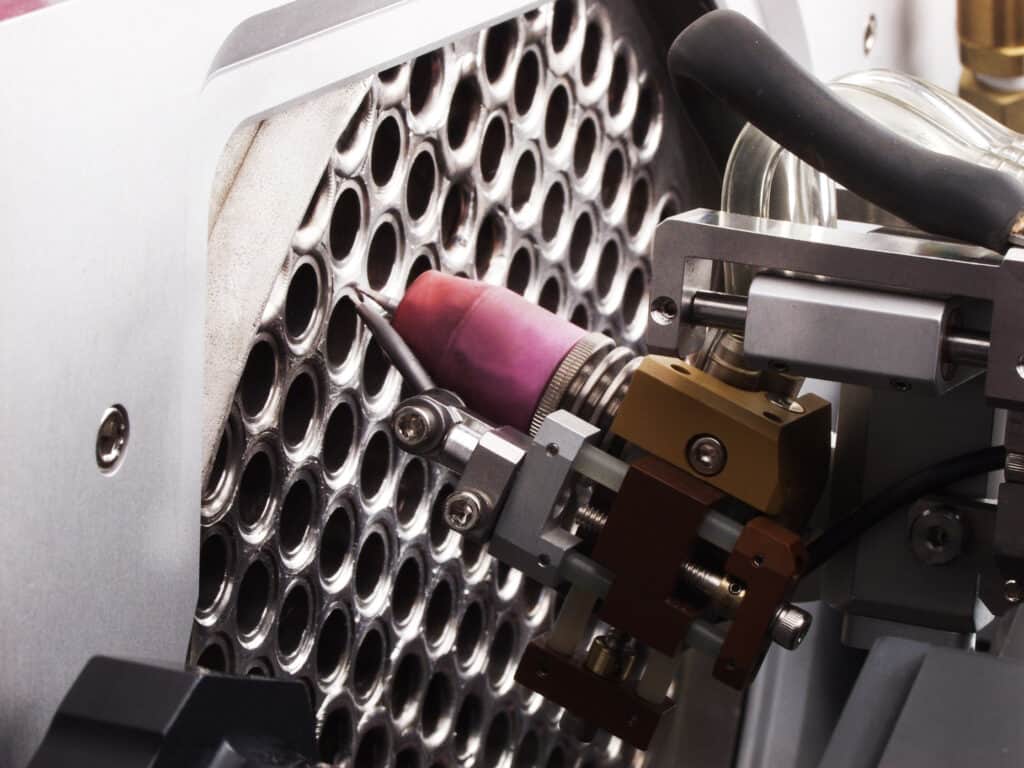
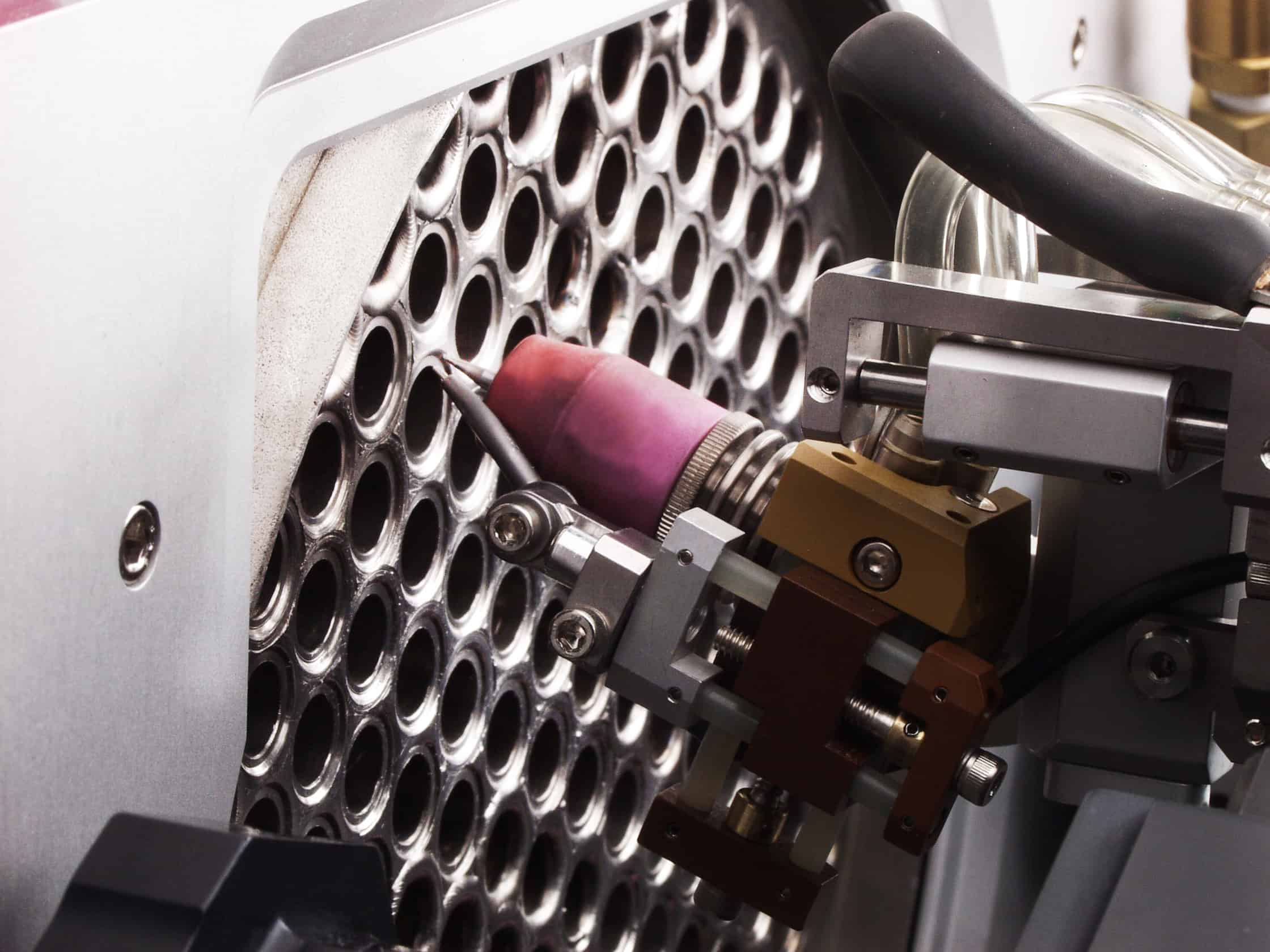
Welding Cobots
The history of welding automation dates back to 1962 when General Motors put its first spot welding robot to work. Robotic arms have been going strong ever since. What is a genuinely new advancement in welding technology are welding cobots. These are welding robots that are designed to work alongside workers instead of replacing them.
Advancements in computers and artificial intelligence have made these systems more flexible. Robotic welding arms can be guided through positions manually, and then will repeat the movement patterns. Slight adjustments can be made afterwards to dial in the movement speed and angles to help ensure quality. This allows an individual robot welding cell to fabricate a wide array of assemblies with minimal change-over time.
Welding Networking and Data Collection
The digital transformation in manufacturing has not left welding behind. Weld data monitoring and weld data storage provide a wealth of information that can be used to engineer better products, develop enhanced welding parameters, and streamline the welding process for efficiency.
This sort of networking and data collection over time is one of the most exciting advancements in welding technology. Data about the performance of welding machines can be used to identify any potential maintenance issues before they cause a work stoppage, and performance data can be analyzed to single out any potentially flawed workpieces. Not only is this immediately applicable in the here and now, this data can also be analyzed to develop improved welding methodologies.
Advancements in welding technology like flexible automation through welding cobots, and improvements in performance like weld networking hold the promise of making welding more efficient and cost effective. They also make welding more accessible to a wider group with less training. Cobots remove the need for extensive training to cultivate muscle memory and stability that is important for manual welding while weld data collection can better inform weld parameter development directly on the shopfloor. Removing workers from the direct vicinity of welding also improves welder and worker safety.
How Advancements in Welding Technology Improve Safety
Manual welding is a hot and uncomfortable job by any standard. It can also be one that has long term health consequences. Stainless steel is a widely used metal in any application where clean and sanitary welds are needed. It unfortunately releases large amounts of a potent carcinogen —hexavalent chromium—when it is heated. Avoiding hexavalent chromium in welding requires substantial amounts of ventilation, and since the welder has their face only a few inches from the arc the ventilation may not be as effective as intended.
Welding automation moves the welder away from direct exposure to the heat and molten metal of welding. It also helps the welder avoid fumes or toxins released due to the heating of the metal. This makes for a safer and more comfortable welding environment, and welders that live longer and more comfortable lives. Advancements in welding technology are sometimes treated like a threat to a worker’s livelihood. Automated welding processes like orbital welding are not hard though, and learning to work with this automation and other advancements in welding technology will enhance a welder’s comfort and ability to work in a range of industries as well as increase their productivity.
Arc Machines, Inc. is an industry leader in orbital welding systems and making advancements in welding technology, welding data, and weld engineering. To learn more from our experts in orbital GTAW welding contact us.