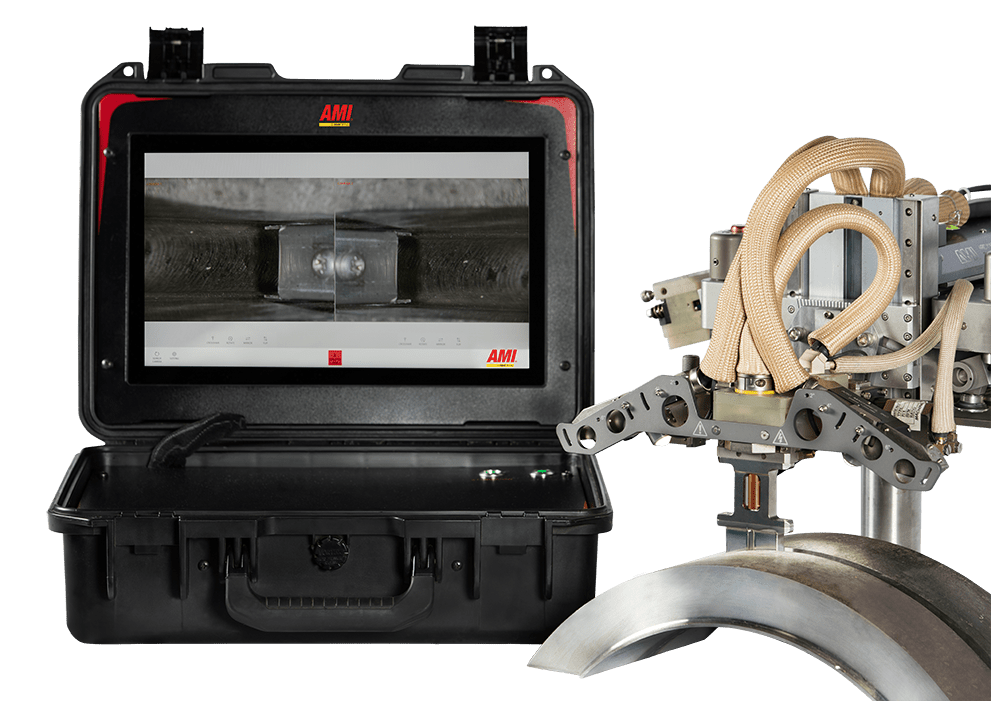
If you’re wondering how to record a weld puddle, you’re not alone. Nearly every welder at some point in their career has had a compelling reason to record or review a recording of a welding procedure. Though nothing replaces hands-on experience, an apprentice welder can use a recording to observe proper techniques and best practices or to compare the results of good and bad welding techniques. Using a camera to view or record a weld is particularly useful for orbital welding procedures in several circumstances. It enables management of remote welding in hazardous environments, giving the welder a real-time view of weld head activity while the process is monitored from a safe location.
In many orbital welding situations, the weld head obscures the welding process. Compact weld heads offer visual access to areas which are difficult for the welder to view. Video can also form part of the welding quality control process by acting as evidence that the weld was completed correctly. Video monitoring gives the welder a clearer, more detailed view of the interaction of electrode, arc, materials, and other factors that determine weld bead quality. In this post, we’ll discuss ways to record a weld puddle as well as what to look for in visual weld monitoring equipment.
To Monitor or Record a Weld, Start With Equipment Designed for the Job
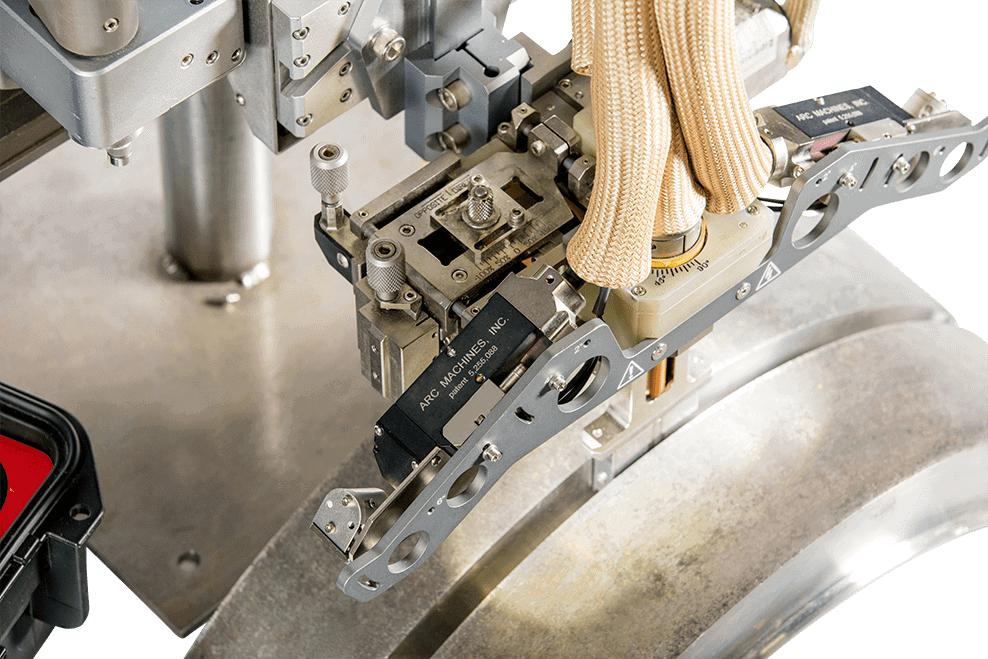
The extreme heat and light associated with orbital welding and the constrained area of some welding operations require monitoring and recording systems specifically designed for the job. High-quality welding vision systems should offer the following features:
- Cameras designed for weld monitoring: The extreme temperatures and radiated heat from a weld require cameras that can tolerate the harsh environment. A water-cooled housing can protect the weld camera from the intense heat of the weld arc.
- High camera and monitor resolution: High monitor resolution and a solid-state charge-coupled device (CCD) in the weld camera should provide enough detail to clearly show any weld puddle issues.
- Versatile, quality optics: The camera’s lenses and digital processor should be designed to filter out specific light frequencies in order to eliminate glare and show a clear view of the weld puddle that is typically better than can be observed through a welding helmet. A variety of lens configurations and camera controls should be available to provide different magnifications, fields of view, and focal lengths that allow operators to focus on the most critical areas of the weld process. While some weld cameras have a fixed focal point, choose a welding vision system with an adjustable focal point. The best cameras will automatically compensate for light intensity differences between welding and non-welding modes.
- Configurability: The weld camera systems should be adaptable to a variety of weld heads and welding applications, from large pipe welds to small precision assemblies. Proper camera angle relative to the weld head is critical in monitoring the weld puddle quality.
- Illumination: The torch isn’t always running and there are times you may want to observe the welding area prior to the weld or after it takes place. Since weld heads can block ambient light, you’ll want to make sure the camera components can provide proper illumination (typically using LED lighting) of the weld area.
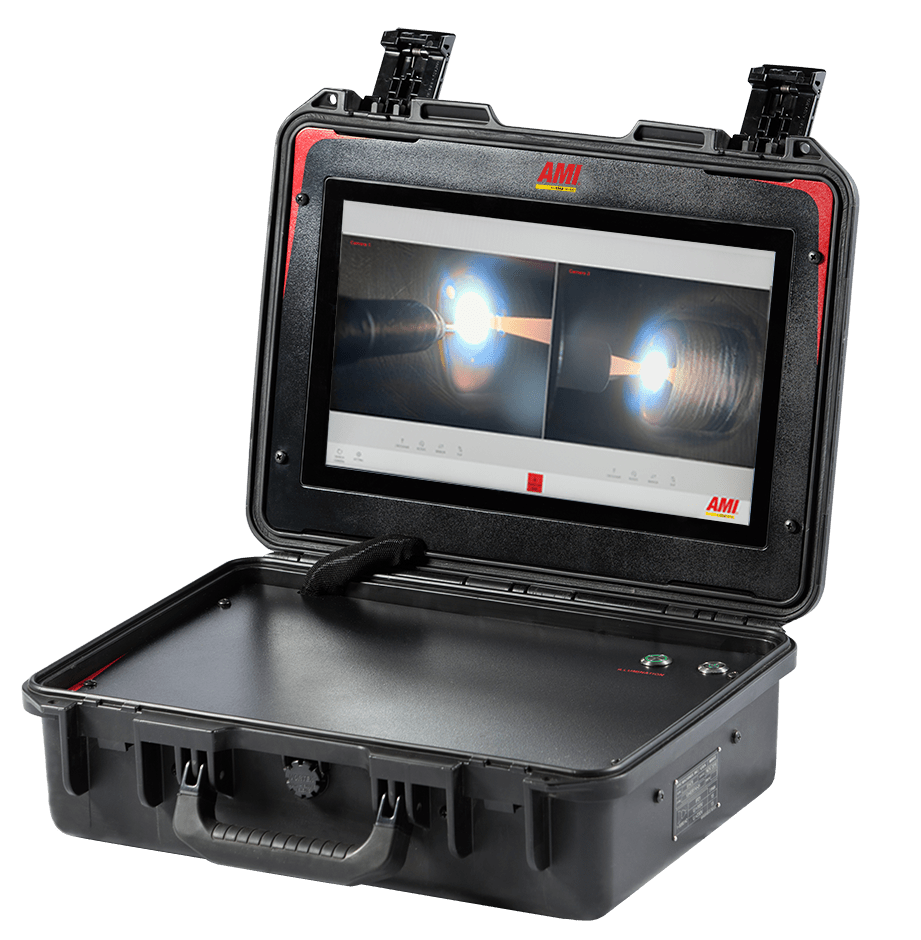
- Recording: Camera systems should integrate with your welding controller to simplify the monitoring and recording of the welding process. Systems that record the date and time provide additional means of process verification in support of quality control and compliance. Some weld cameras (such as Arc Machine’s M802-DV) can take a still image of the weld as well as record video.
- Remote monitoring: In hazardous environments, camera control and cooling cables that span the distance between the controller and welding head facilitate safe observation of the weld.
- Compact Design: New technology makes it possible for cameras to be smaller and in some cases can allow cameras to be added to older orbital welding machines. A smaller design also makes it possible to use cameras in orbital welding system designs that weren’t previously compatible with cameras.
A well-designed weld monitoring system has the versatility to adapt to a wide range of welding applications. As with any new technology or system, it’s worthwhile to invest time in setting up a test environment prior to using the system for production-level monitoring and recording.
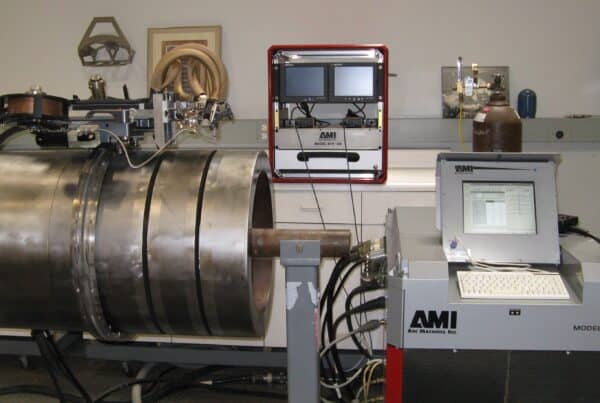
Testing a Weld Vision System

Obtaining a quality recording of a weld puddle will require some preparation to optimally configure the camera in relation to the weld head. Use several test pieces for trial runs as you fine-tune the camera location, angle, and optics to capture the weld puddle detail.
Camera position and focus will be determined by which aspects of the welding process you want to monitor with respect to their effect on the weld puddle. You’ll want to consider the following questions as you refine your camera setup:
- Should the cameras focus on the weld puddle’s leading edge, trailing edge, or both?
- Which potential defects do you intend to identify: porosity, wet out fluidity, lack of fusion, undercut, evidence of burn-through?
- Is torch alignment affecting weld quality?
- Are shielding gas interference, filler wire, or material defects resulting in porosity?
- How does the filler wire feed rate or position affect weld quality?
- Does the welding area need illumination when the torch is not operating?
- Which view—color or monochrome—provides the best weld puddle image for monitoring the process?
Working with several test pieces will give you a sense of the camera’s capabilities and help you determine which camera setup provides the best detail for the weld puddle aspects that need to be monitored. Once you’ve determined the best way to record a weld puddle, you can then apply this knowledge to a wide range of welding applications that benefit from real-time monitoring and recording.
Benefits of Learning How to Record a Weld Puddle
There are distinct advantages to recording a weld puddle using weld monitoring equipment. Regardless of the operator’s visual acuity, a purpose-built weld vision system has the technology and capability to provide a clearer image of the welding process. Camera technology allows the operator to focus on aspects of the process that affect weld puddle quality. Whether the purpose is to record a weld for teaching or learning new techniques, or to monitor the process for quality assurance or operator safety, weld monitoring equipment can become an indispensable tool for welders intent on ensuring the quality and reliability of the work they undertake.
Arc Machines, Inc. is a leader in orbital welding, with experienced employees, innovative products, and video systems specifically designed to monitor a wide range of welding processes. For inquiries regarding products, contact sales@arcmachines.com. For service inquiries, contact service@arcmachines.com. Arc Machines welcomes the opportunity to discuss your specific needs. Contact us to arrange a meeting.




