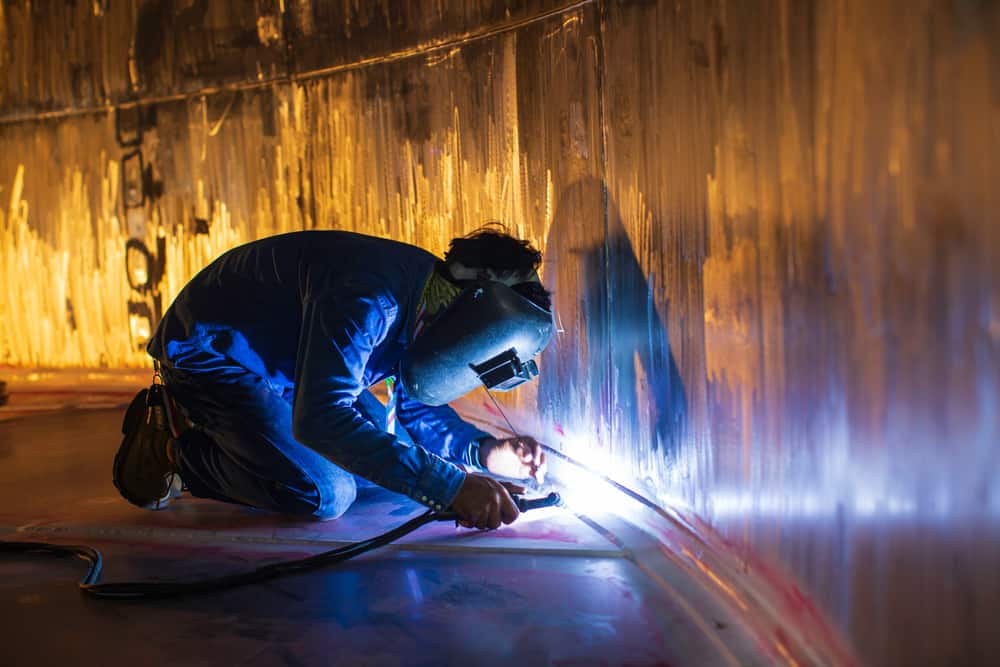
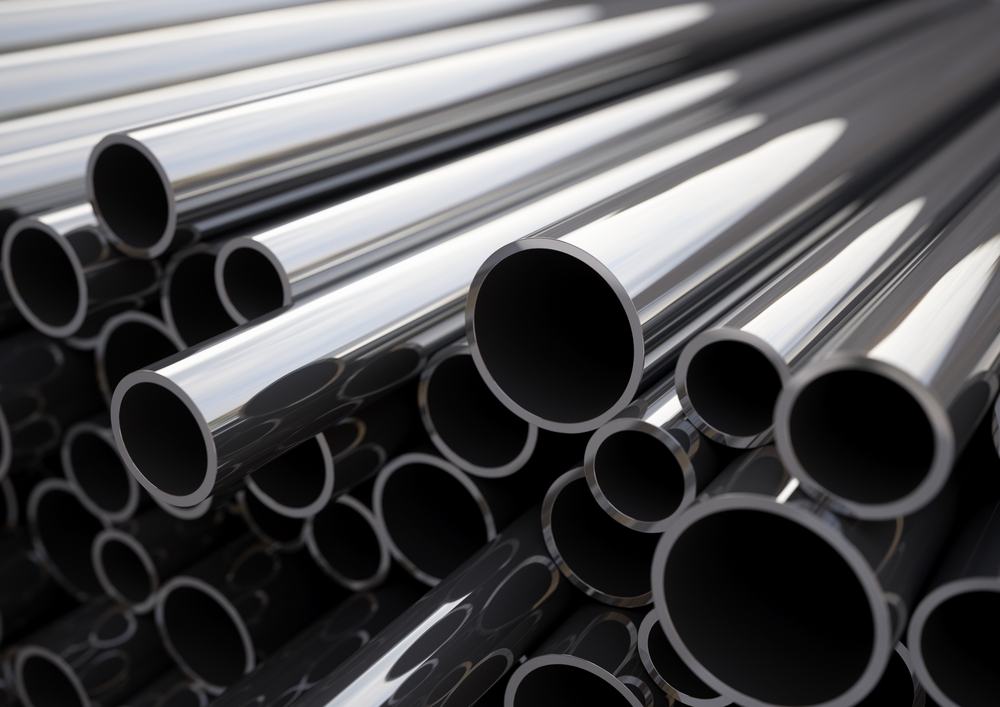
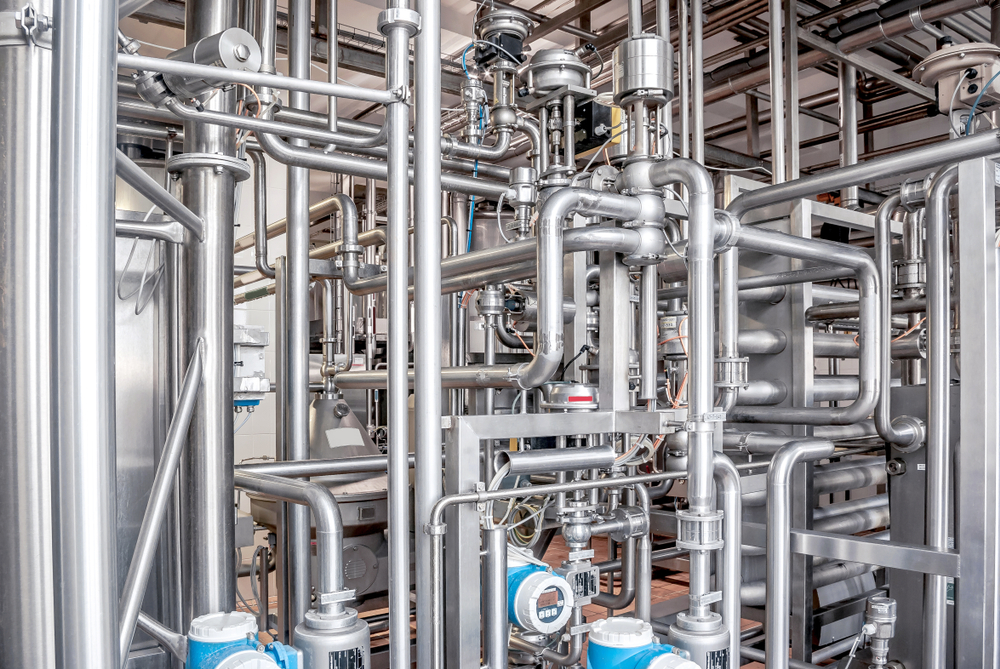
Steel tubing is used everywhere—from refineries to aerospace to pharmaceuticals. It safely and reliably transports process fluids from one point to another. When welding steel tubing, welders have to make sure that the mechanical properties of the metal are not compromised so it can fulfill the reason for use in…