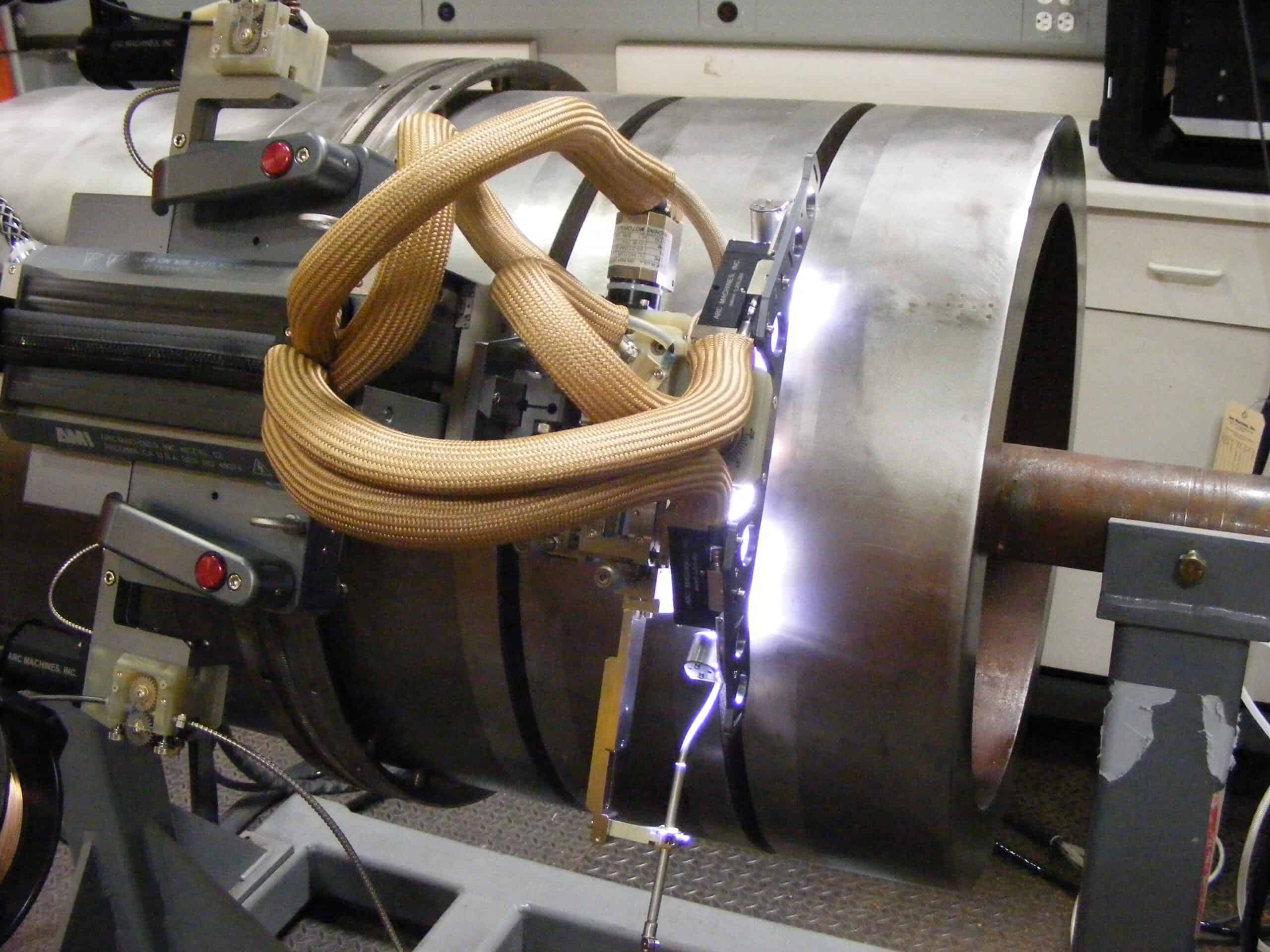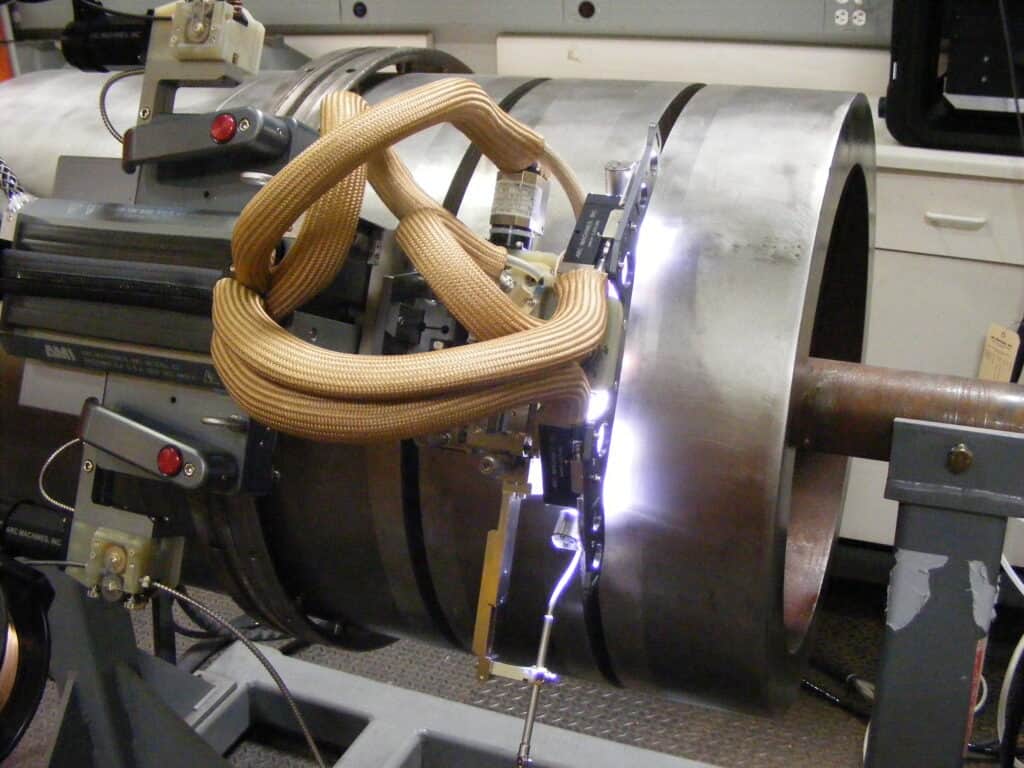
Applying manual welding skills on critical weld projects requires years of technical training and experience. And the process can still result in slow speeds, reduced productivity, and even worker injury. Also, any weld defects—like those that result from welder fatigue—must be addressed. Compared with the effort manual welding requires, orbital welding offers a more efficient and productive solution where an automated system performs much of the work.
However, operators should apply best-practice techniques to achieve the optimal orbital welding results. This article will discuss the various orbital welding techniques that differentiate the process from other automated welding processes.
Orbital Welding Techniques
Orbital welding designates a mechanized welding process that allows the complete 360° rotation of the arc around the stationary workpiece. This welding option is most beneficial for pipes or tubes, where welding in different angles, positions, and clearances can present an issue. The automated process offers excellent parameter control and repeatability and, as a result, allows operators to achieve the best weld result in every weld cycle.
Because automation resides at the core of orbital welding, the orbital welding technique might seem obvious. In tube welding applications, for instance, the orbital welding technique may simply require the operator to push a button to accomplish the task. However, if we consider narrow groove welding, the orbital technique greatly depends on the operator’s ability to monitor the molten puddle and intervene when a weld adjustment is required to keep the metal flowing and fusing correctly.
Techniques that make orbital welding efficient and productive include proper weld preparation and monitoring.
Weld Preparation
The preparation procedure directly influences the quality of the weld. This is especially important in the joint preparation of pipes or tubes. From basic steps like removing grease and rust to machining the parts to create an appropriate groove, weld preparation allows orbital welding to produce a more refined result. Some preparation techniques may include:
- Bevelling the pipe ends for better weld penetration in larger weld thicknesses.
- Removing burrs for even ends without distortion or damage.
- Utilizing standard V or J preparation for orbital welding for joints without gaps.
- Provisioning for appropriate welding gases such as argon or a mixture of argon with hydrogen and helium.
- Provisioning for adequate back purging so that the proper “ID” gas can provide the best result during root pass or subsequent hot pass.
- Utilizing standard V or J preparation for orbital welding for joints without gaps.
- Preheating the weld material to enable slow cooling during welding and reduce the chances of hydrogen cracking.
Another preparation requirement focuses on welding tools and setups. While tools such as weld heads and controllers should be compatible with the type of welding desired, care should also be taken to prevent pipe misalignments.
Weld Monitoring
In applications such as narrow groove welding for sidewall fusion, monitoring is an important aspect of quality control. Usually, a weld camera for orbital welding provides a real-time inspection opportunity to ensure complete weld coverage. Weld parameters, such as weld head alignment, feed rate, and shielding coverage, can also be easily monitored and optimized for defect prevention and better weld quality.
While orbital welding is predominantly an automated process, the result is not solely dependent on automation but also preparation, setup, and monitoring. Procedures often require timely manual interventions.
Orbital Welding Is the Favored Welding Option
Even with adequate weld preparation, there are challenges associated with manual welding. The risk of human error, the ergonomic challenge of different welding positions, and reduced productivity, being a few of them. Orbital welding eases these challenges by automating difficult welding jobs that can be risky or require impeccable control. Relying on automated processes that can weld across all orientations and welding environments can enable more consistent and reliable welds. Weld prep, setup, and monitoring are integral orbital welding techniques that support automated processes to ensure high-quality results. Ultimately, the unique collaboration between automated systems and operator monitoring makes orbital welding the preferred option.
Arc Machines, Inc. has decades of experience in creating orbital welding solutions that suit the welding needs of our clients. To learn about the orbital welding techniques and develop a custom orbital welding procedure, contact us to arrange a meeting.