All welding processes produce emissions, including heavy metal fumes and chemicals, as the metal becomes molten. Exposure to this fume for an extended period increases the risk of serious health-related issues to welders. In a more enclosed space, this risk is even greater. As a preventive measure, proper welding ventilation is required for any welding process. Industries are increasingly adopting advanced welding technologies with an effective ventilation system to protect welders.
One such technology is orbital welding. Its automated system keeps welders away from the fume source and facilitates welding ventilation to minimize the risk of exposure.
Risks Associated With Welding Emission
Welding emissions comprise visible and invisible fumes and gases produced during the welding and cutting process. The composition and toxicity of these fumes and gases vary depending on the type of metal, coating on the metal surface, and the composition of the electrode. The resulting fumes may include hazardous substances that are toxic or carcinogenic and can damage the respiratory system. For example, a welder working with stainless steel can be exposed to toxic hexavalent chromium, known to cause cancer.
Some examples of the types of hazardous substances welders may be exposed to during the process include:
| Lung Damaging Substances | Poisonous / Toxic Substances | Carcinogenic Substances |
| Aluminum oxide Iron oxides Magnesium oxide Titanium dioxide | Manganese dioxide Carbon monoxide Carbon dioxide Copper oxide Nitrogen oxide Phosgene Zinc oxide | Chromium compounds Lead oxide Formaldehyde Nickel oxide Beryllium oxide Cadmium oxide Cobalt oxide Ozone |
The composition of metals and coatings are not the only factors that produce welding emissions. The welding process and its parameters also contribute to such emissions. For instance, higher welding current and voltage results in an increased amount of fume production. DC welding is associated with stable arc and smooth welding, resulting in less emission than AC welding. The size of the electrode also affects the amount of weld emissions. A larger electrode diameter creates more emissions.
Controlling these factors by providing proper welding ventilation is a key component in protecting welders from exposure to hazardous fumes.
Welding Ventilation for Reduced Risks
The provision for welding ventilation in the work area depends on the welding environment, the number of welders in that area, the dimension of the workplace, the types of fume emissions, and the welder’s proximity to the emission source.
Organizations like Occupational Health and Safety Association (OSHA) have recognized the risk of welding fumes for welders and require industries and workers to follow safety protocols to reduce the potential health effect. One of those safety measures is the provision for welding ventilation. In a confined space:
- Mechanical ventilation is required if the welding area is less than 10,000 cubic feet per welder and ceiling height less than 16 feet.
- Mechanical ventilation should not obstruct the cross-ventilation system or interfere with the welder’s ability to perform the task easily.
- The ventilation system should not block the entry and exit access to the workplace as well as their ability to access any ramp, elevators, or ladders in the vicinity.
Depending upon their ventilation needs, industries can make provisions for:
| General ventilation | Not adequate in preventing risks for welders. Can be used when arc welding / TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding in outdoor areas. |
| Local mechanical ventilation system | Required for MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding / TIG welding in confined spaces, open work floor, or outdoors. May include ventilation hose, movable hoods or ducts that can be placed near the welder, or fixed enclosures surrounding the weld area with adequate velocity to extract the fumes away from the welder. |
Regardless of the type of ventilation system, it should accomplish the following objectives:
- Contain the fumes immediately near the point of origin.
- Prevent oxygen deficiency in the work area.
- Ensure smooth and safe workflow.
To achieve these safety goals without decreasing productivity, industries are adopting advanced automated technology such as orbital welding.
Orbital Welding for Improving Safety
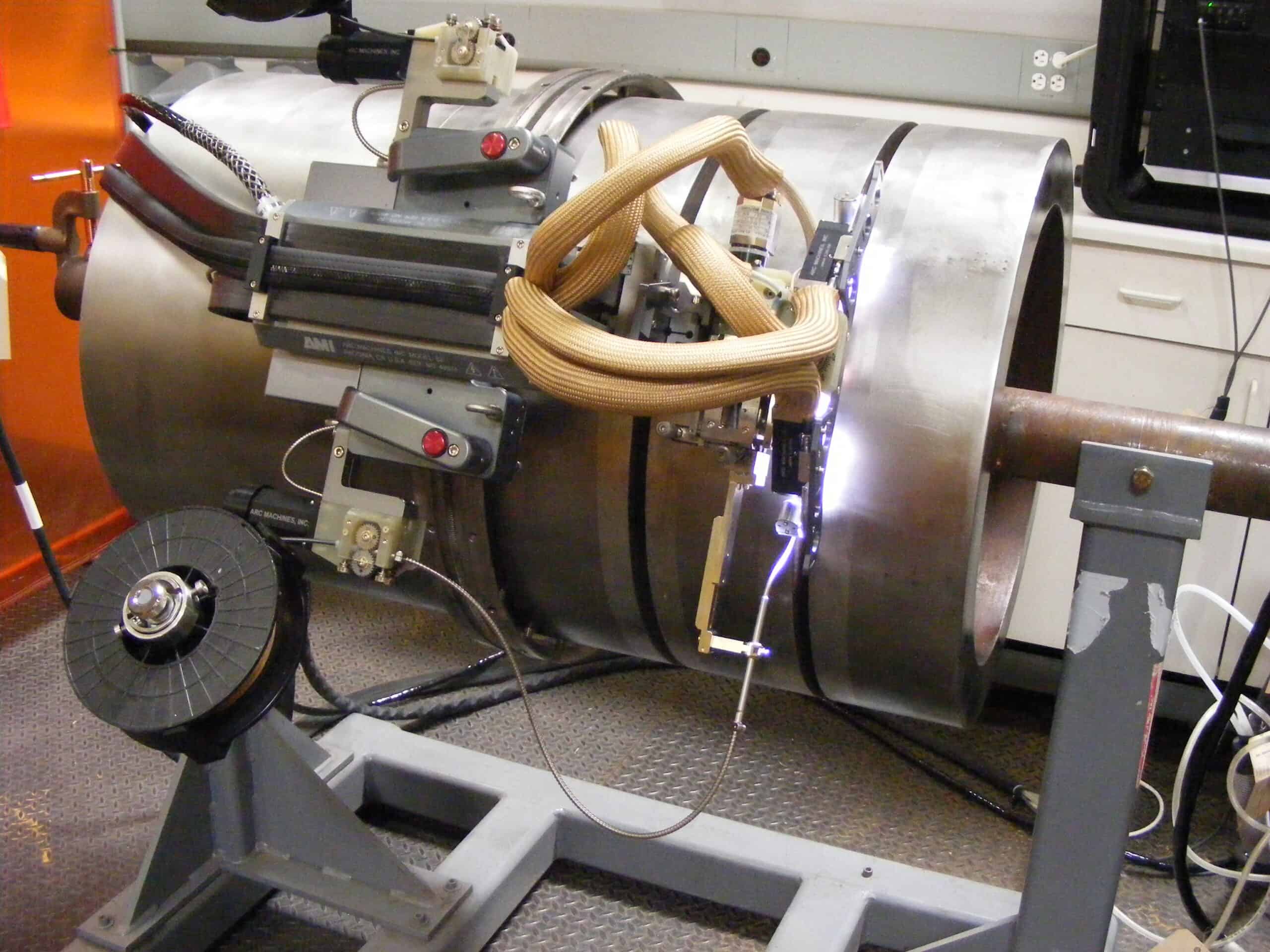
Orbital welding is an automated welding system where the auto weld heads move around the stationary workpiece to create a precise and consistent weld. An automated process allows optimization of parameters such as arc length, feed speed, voltage, and current. Operators can set the parameters to ensure the welding process emits as few fumes as possible. These parameters can be controlled with the help of a weld pendant, which allows remote monitoring, minimizes defects, and produces high-quality welds. With careful planning, remote operation allows manufacturers to virtually eliminate the health-related risks associated with welding because operators are not in immediate exposure to the welding fumes.
Arc Machines, Inc. is a leader in orbital welding technology with decades of experience and expertise. With solutions like AMI orbital weld heads and remote weld pendants, we help industries improve their welding ventilation system while producing high-quality weld results. Contact AMI to learn more about training or contact sales@arcmachines.com for more information.