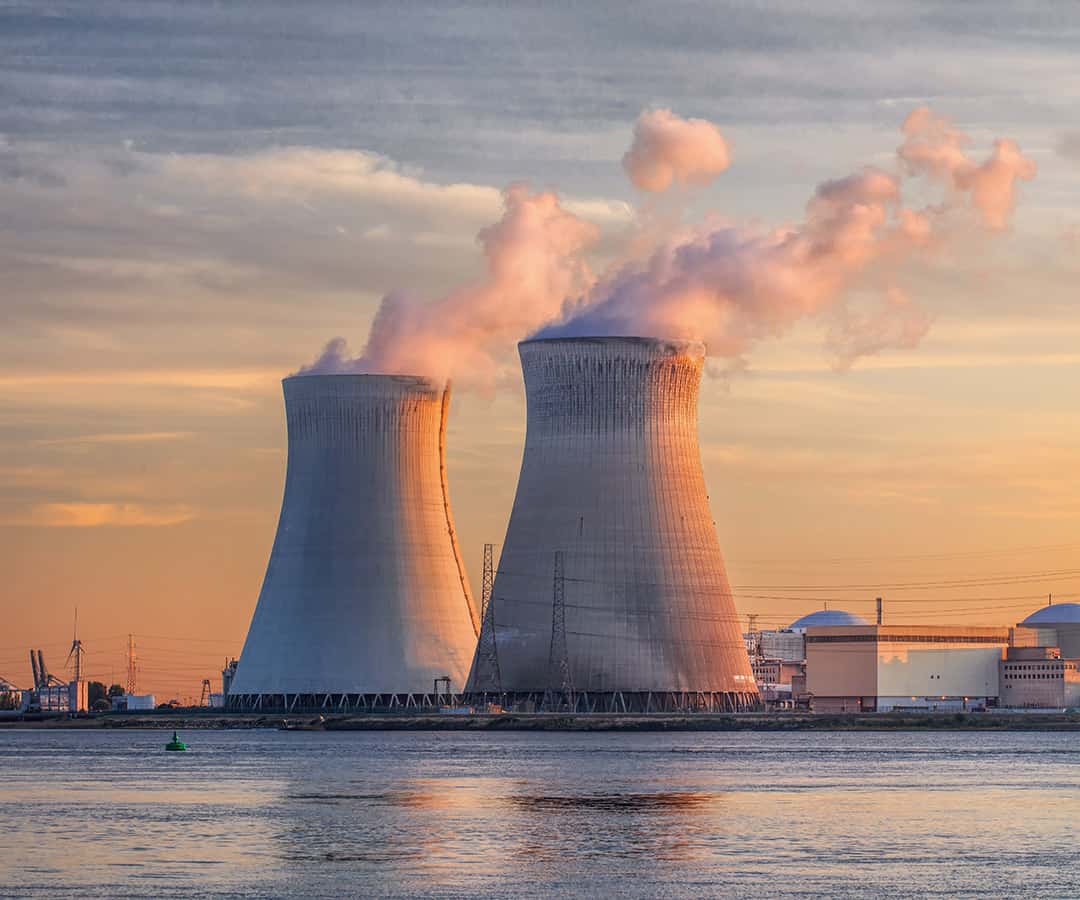
The extensive welding of pipes, tubes, and vessels in the nuclear industry introduces unique challenges. From material selection to potential weld defect analysis, nuclear welding must meet quality standards through each step of the process.
Proper Material Selection
Given the extreme conditions in nuclear power plants, proper material selection is critical to prevent degradation. Nickel alloys (Inconel®), stainless steel, and copper alloys are generally preferred for their sound mechanical properties, weldability, and corrosion resistance.
Corrosion Prevention
Corrosion threatens the lifespan of nuclear plants and can cause billions of dollars in damages. Materials—especially near the welded joints—are susceptible to corrosion and cracking due to the extreme conditions at the nuclear reactor. The table below discusses the types of corrosion likely to occur in nuclear welding and their potential causes.
In the nuclear industry, even microscopic defects possess a high level of risk. And while material selection is imperative to maintain vessels, pressurizers, and storage tanks, choosing the right welding technique is just as important.
Adherence to Critical Nuclear Welding Standards
Safety is the top priority in the nuclear industry, and the industry is required to adhere to a strict set of rules and standards for safe operation and quality assurance during the construction and operation of nuclear handling sites. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) Section III details the quality requirement for components in nuclear power plants. Other quality-assurance bodies include ISO 3834 which provides welding best practice details for metals and ensures quality adherence for national and international use.
Automated welding processes such as orbital welding have allowed the nuclear industry to overcome these safety challenges while improving weld quality and reducing costs.