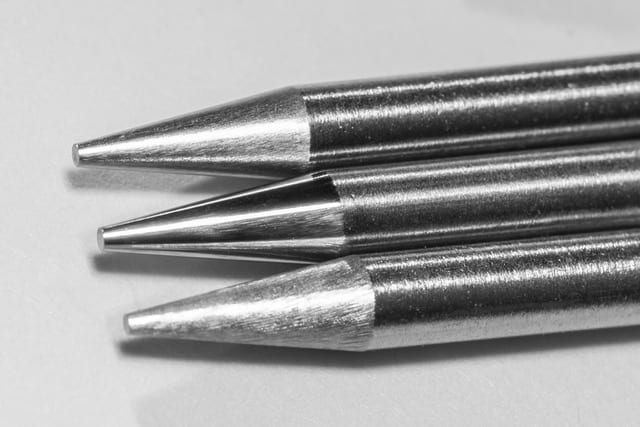
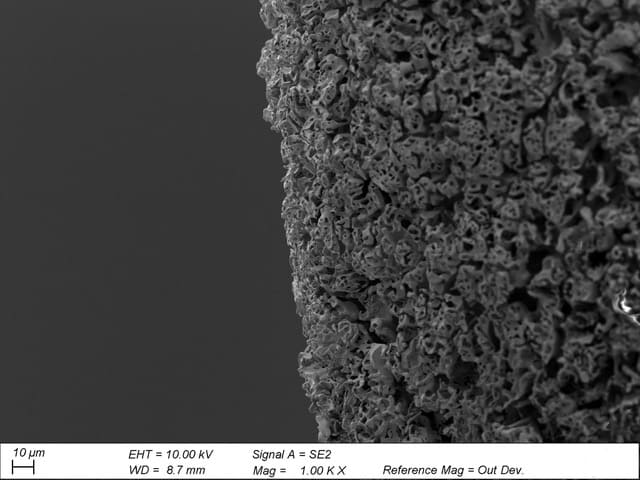
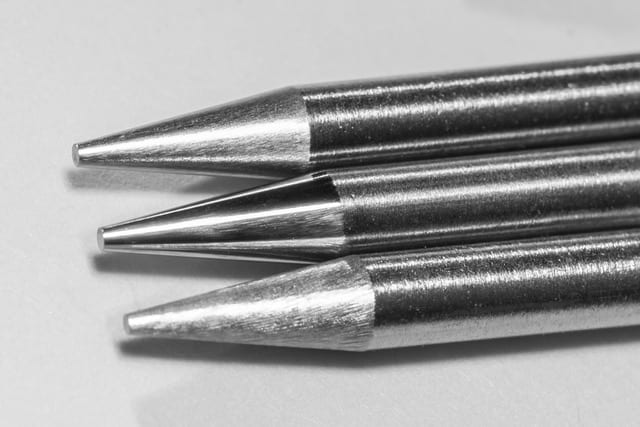
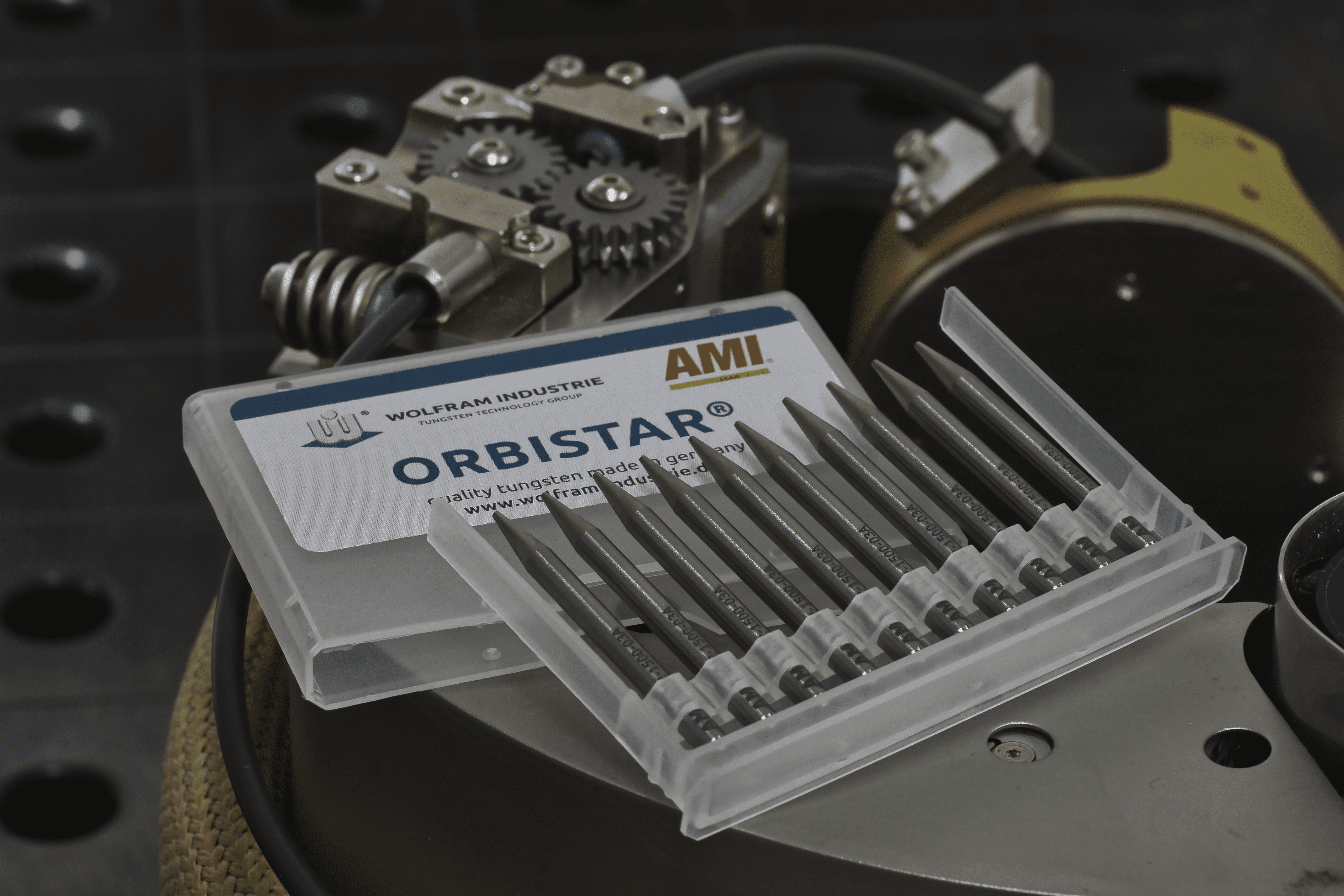
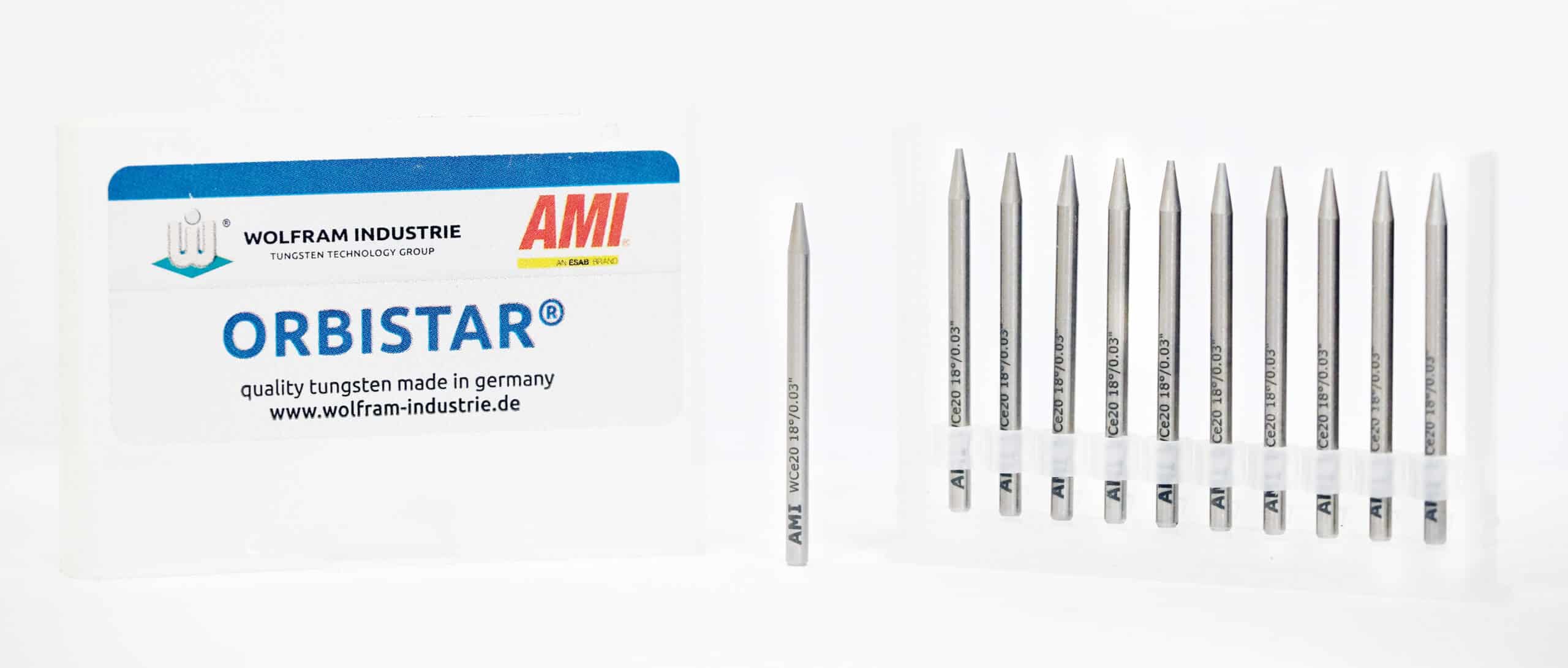
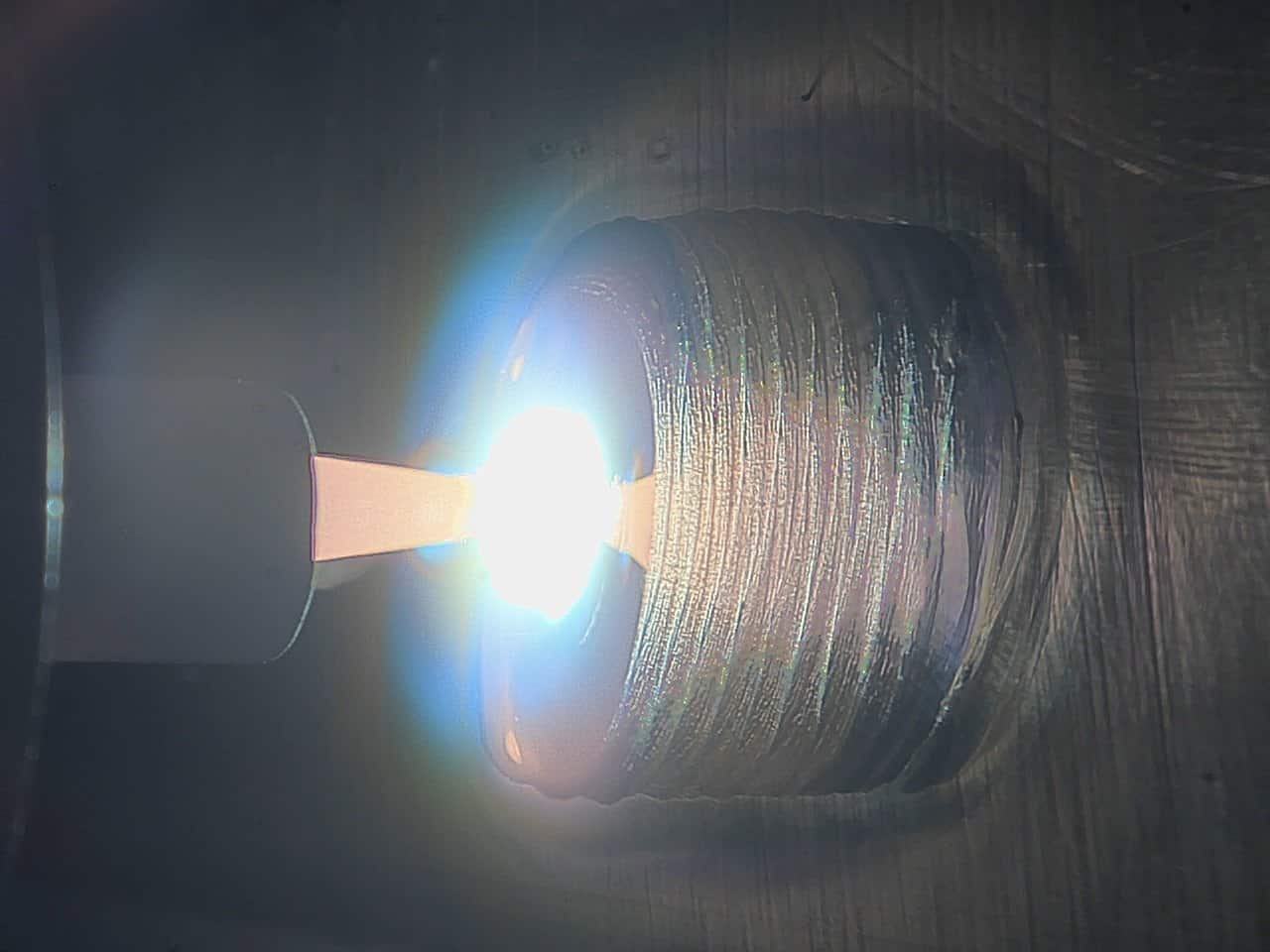
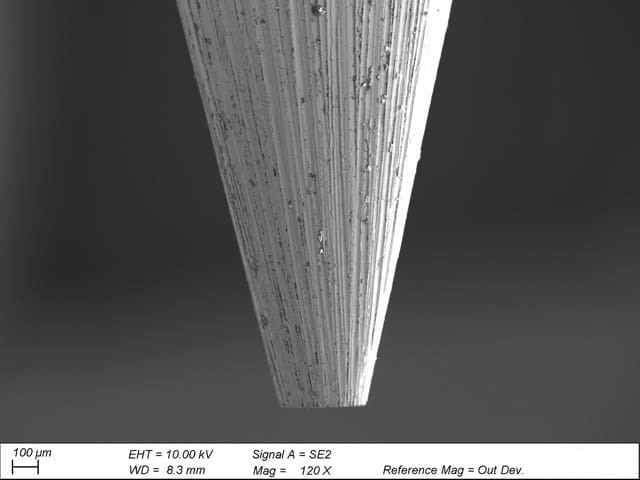
Tungsten inclusion is a welding defect found in gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding. This welding process uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to generate an arc—and a tungsten inclusion occurs when some of the material from this electrode is deposited into the molten…