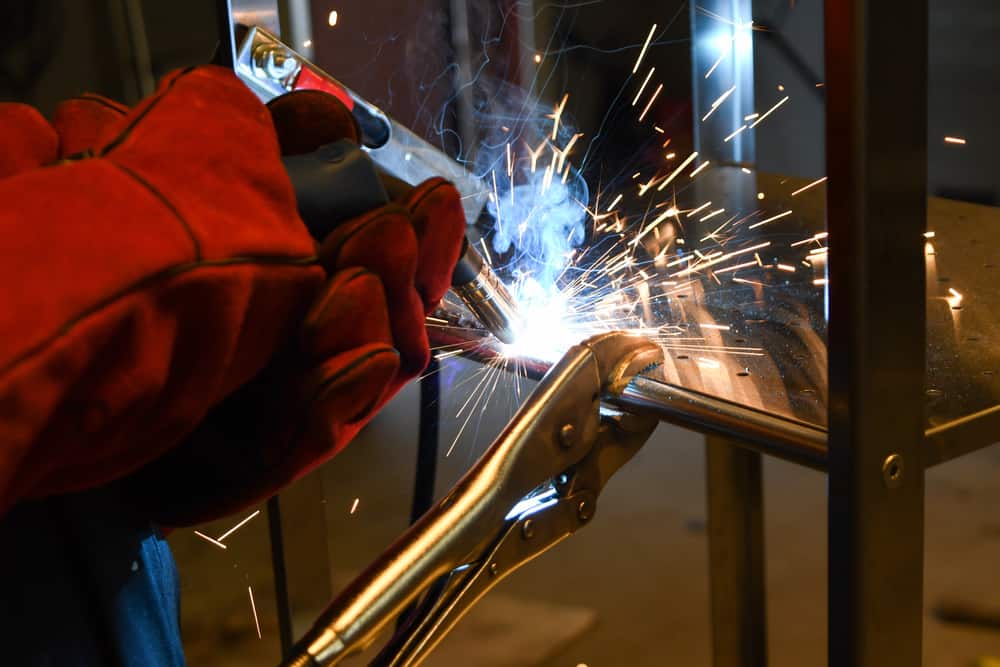
Every year, the welding industry spends millions of dollars in compensation for welders exposed to harmful substances. Carcinogenic substances in welding fumes, such as hexavalent chromium, represent a primary health concern in the welding industry. To protect welders from being exposed to these toxins, industries must follow various safety procedures and ensure the availability of protective equipment and welding ventilation systems.
As a more advanced form of control, industries are also using automated welding systems such as orbital welding. With an automated system, welders are safe from direct exposure to harmful substances and the resulting health effects.
With an automated system, welders are safe from direct exposure to harmful substances and the resulting health effects.
Hexavalent Chromium and Its Associated Hazards
In the workplace, welders can be exposed to hexavalent chromium—also known as Chromium 6, Chrome 6, or Cr (VI)—when working with sources such as:
- Fumes from stainless steel or other chromium alloys
- Dyes, inks, paints, primers, or other surface coatings with chromate pigments
- Chromium-plated metals
A high percentage (11.5- 30%) of chromium is added to steel to enhance its hardness and corrosion-resistant properties. While chromium itself may not be very hazardous, when exposed to heat during processes such as welding, it can oxidize to form hexavalent chromium which is carcinogenic. These microscopic substances enter the human body during inhalation, dissolve with water inside the body, and change into trivalent chromium, which can cause long-term health effects such as asthma and ulcers. It can even harm the body at the cellular level, potentially causing autoimmune diseases and cancer.
To reduce these risks and minimize a welder’s exposure to hexavalent chromium during hot working of stainless steel or other chromium alloys or surface coatings, organizations like OSHA require employers to maintain strict safety standards.
Regulations for Minimizing Risks
The Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) has introduced many regulations that aim to reduce occupational exposure to hexavalent chromium.
- For an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) in a 40-hour workweek, the exposure of chromium compounds should be limited to 5 micrograms or less of hexavalent chromium per cubic meter of air.
- Preventive monitoring should be performed every 6 months if the initial monitoring indicates the hexavalent chromium exposure to be at or above 2.5 micrograms per cubic meter of air on 8-hour TWA.
- Manufacturers should provide proper protective equipment as well as a proper ventilation system to capture fumes at the source.
Besides these regulations, OSHA also emphasizes changing engineering controls and work practices to help minimize exposure. Industries are actively adopting advanced technology to reduce the risk of exposure to welders with automated welding technologies like orbital welding.
Automated Welding Minimizes Exposure
Automated welding systems such as orbital welding reduce the risk of exposure to Hexavalent Chromium because a process like orbital welding can eliminate a welder’s direct exposure to harmful substances. Automated systems use auto weld heads and remote pendants to perform and optimize the actual weld—systems that allow operators to conduct monitoring tasks remotely while optimizing weld parameters such as arc length, voltage, current, and feed speed. Operators can work from a risk-free location and eliminate the direct health risks associated with exposure to hexavalent chromium.
Arc Machines, Inc. is a leader in providing automated welding solutions with decades of experience and expertise in orbital welding technology. With solutions like AMI orbital weld heads and remote weld pendants, we help industries minimize the exposure to hexavalent chromium in welding while keeping operators safe to generate high-quality weld results. Contact AMI to learn more about training. For more information, contact sales@arcmachines.com.